Start studying Trigonometric α β θ π a² √ Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study toolsIf 5 secθ – 12 cosecθ = 0, find the values of secθ, cosθ and sinθ Let n ≥ 2 be a natural number and 0 < θ < π/2 Then ∫ (sinn θ sinθ)^1/n cosθ/(sin^n1θ) dθ is equal to (where C is a constant of integration) asked in Mathematics by Niharika (756k points) jee mains 19;

Part Iii Given Sin 8 1 2 And Frac P 2 Gauthmath
Cos(θ+π/2)=-sinθ 证明
Cos(θ+π/2)=-sinθ 证明-Cos (θ−π/2)=cosθ・cosπ/2sinθ・sinπ/2=sinθ 同値ですので cos (π/2−θ)=cos (θ−π/2) cos (−θ)=cosθというようにcosは偶関数なので ()内の値の正負を変えても絶対値を代入した値に等しUse trigonometric identities to transform the left side of the equation into the right side (0 < θ < π/2) (1 sin θ)(1sin θ) = cos2 θ (1 sin θ)(1sin θ) = 1 cos2 θ COMPANY




Ex 6 2 9 Prove That Y 4 Sin 2 Cos Theta Is Increasing
Problem Statement ECE Board April 1993 Solve for θ in the following equation sin 2θ = cosθ A 30° B 45° cos T (2 sin T sqrt 3) = 0 well right off pi/2 and 3 pi/2 so what about sin T = sqrt3/2 well then it is a 30,60, 90 triangle and we are talking about the 60 degree corner sin is in quadrants 3 and 4 so pi pi/3 = 4 pi/3KK Gan 2 ω is the angular frequency ω = 2πf, with f = frequency of the waveform frequency (f) and period (T) are related by T (sec) = 1/f (sec1) Household line voltage is usually 1101 V RMS ( V P), f = 60 Hz It is extremely important to be able to analyze circuits (systems) with sine or cosine inputs Almost any waveform can be constructed from a sum of sines and cosines
Then sinθ = x now, sinθ = cos( π 2 − θ) = x and cos−1x = π 2 − θ therefore, sin−1x cos−1x = θ π 2 −θ = π 2 Let, sin−1x = θ;Try IT(トライイット)のθ と θ+(π/2)の関係の映像授業ページです。Try IT(トライイット)は、実力派講師陣による永久0円の映像授業サービスです。更に、スマホを振る(トライイットする)ことにより「わからない」をなくすことが出来ます。全く新しい形の映像授業で日々の勉強の
The second and third identities can be obtained by manipulating the first The identity 1cot2θ = csc2θ 1 cot 2 θ = csc 2 θ is found by rewriting the left side of the equation in terms of sine and cosine Prove 1cot2θ = csc2θ 1 cot 2 θ = csc 2 θ 1cot2θ =(1 cos2θ sin2θ) Rewrite the left side = (sin2θ sin2θ)(cos2θ sin2θ cos (θπ/2) = cos ( (θπ/2)π) = cos (θπ/2) = cos (π/2θ) = sinθ sin (θπ/2) = sin ( (θπ/2)π) = sin (θπ/2) = sin (π/2θ) = cosθ この2式を使って、θ = φπ/2 と置けば、 cosφ = sin (φπ/2) sinφ = cos (φπ/2) それとも、sin, cos をべき級数で定義して、 4式の成立を計算で示して欲しいのか? 2 件 dx/dθ = (cosθ)(cosθ) (1sinθ)(sinθ) = cos^2θ sin^2θ sinθ = cos2θ sinθ dy/dx = 0 where dy/dθ = 0 and dx/dθ ≠ 0 dy/dθ = 0 when cosθ = 0 (θ = π/2, 3π/2) 12sinθ = 0 (θ = 7π/6, 11π/6) dx/dθ = 0 when θ = 3π/2 so y'=0 at π/2, 7π/6, 11π/6 you can verify this from the graph at
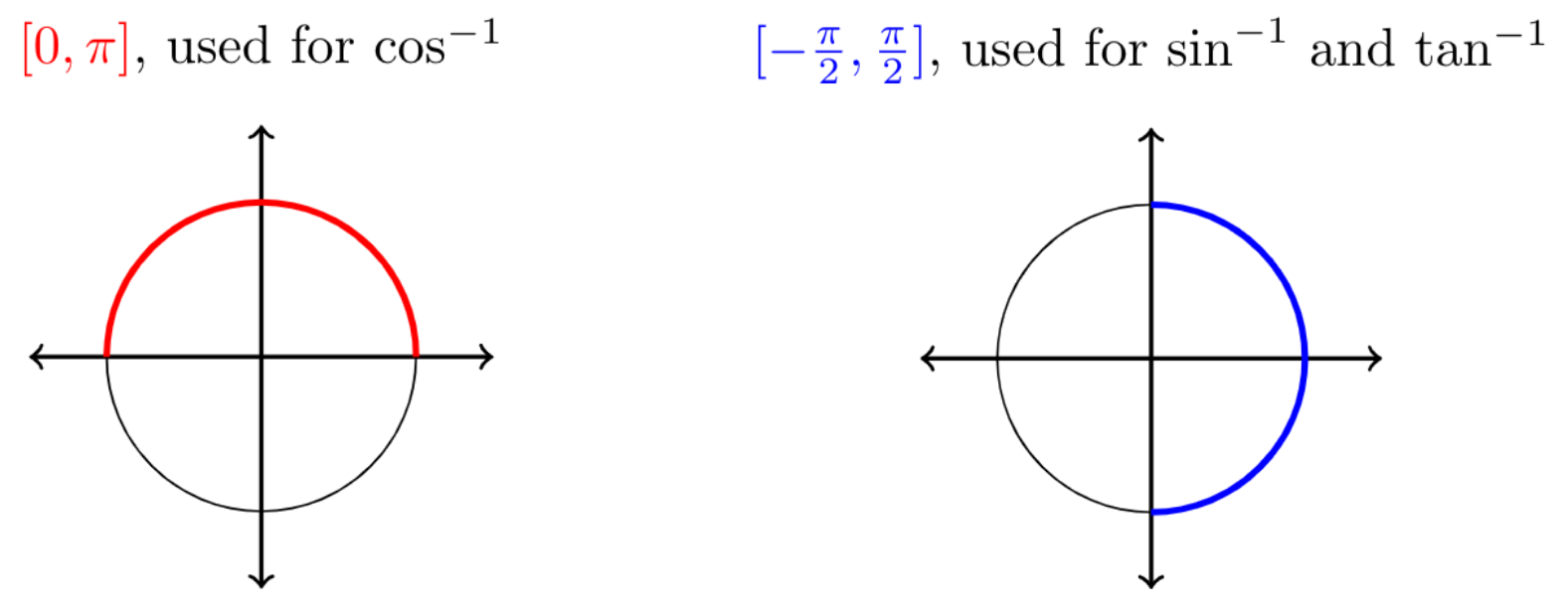



Mfg Inverse Trigonometric Functions
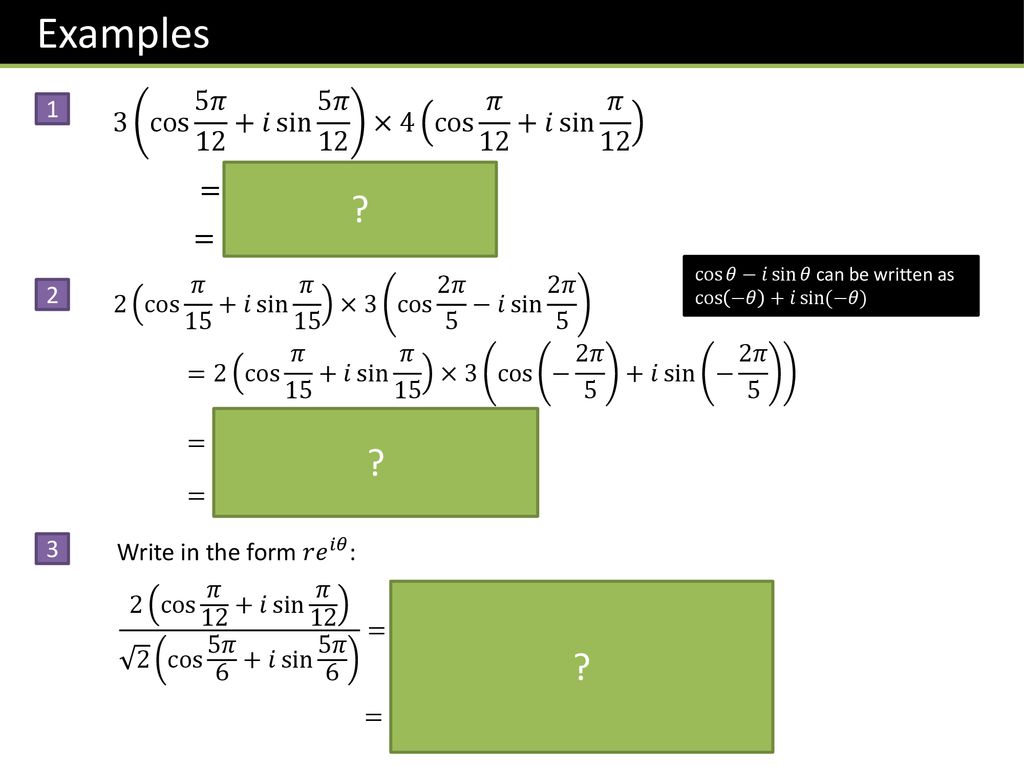



Corepure2 Chapter 1 Complex Numbers Ppt Download
With only the sides given, you'd have to solve for an angle using the law of cosines If the triangle had a right angle, you could use the inverse trig functions The law of cosines is c^2 = a^2 b^2 2*a*c*cos a, b, and c are sides of a triangle, and C is the angle included between a and bθ π 2 = −sinθ cos θ π 2 = cos π 2 cosθ −sin π 2 sinθ, using cos(uv) = cosucosv −sinusinv = (0)cosθ −(1)sinθ, using the unit circle to evaluate the trig functions of pi/2 = −sinθ Page 2 of 40 votes 1 answer
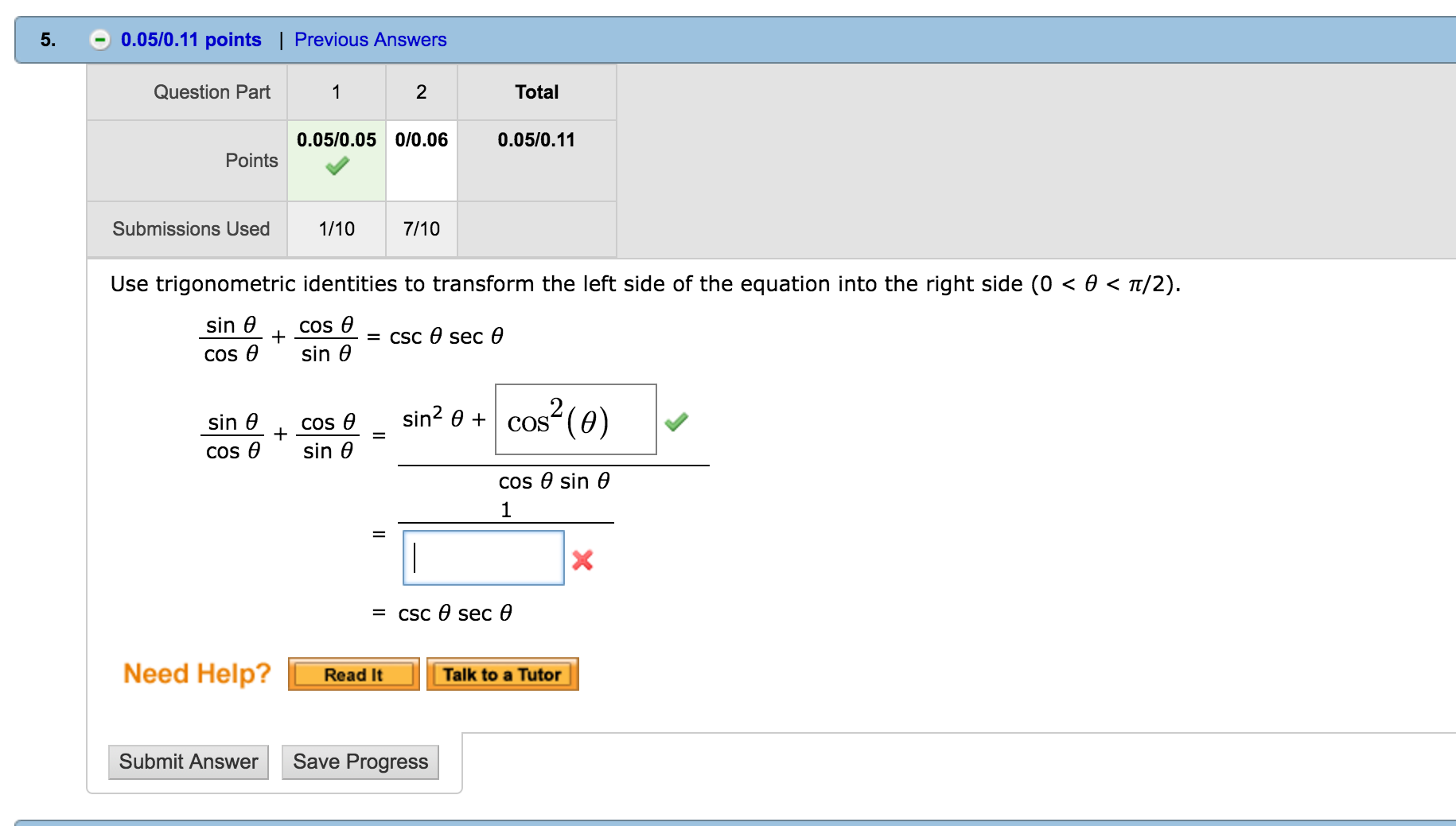



Use Trigonometric Identities To Transform The Left Chegg Com
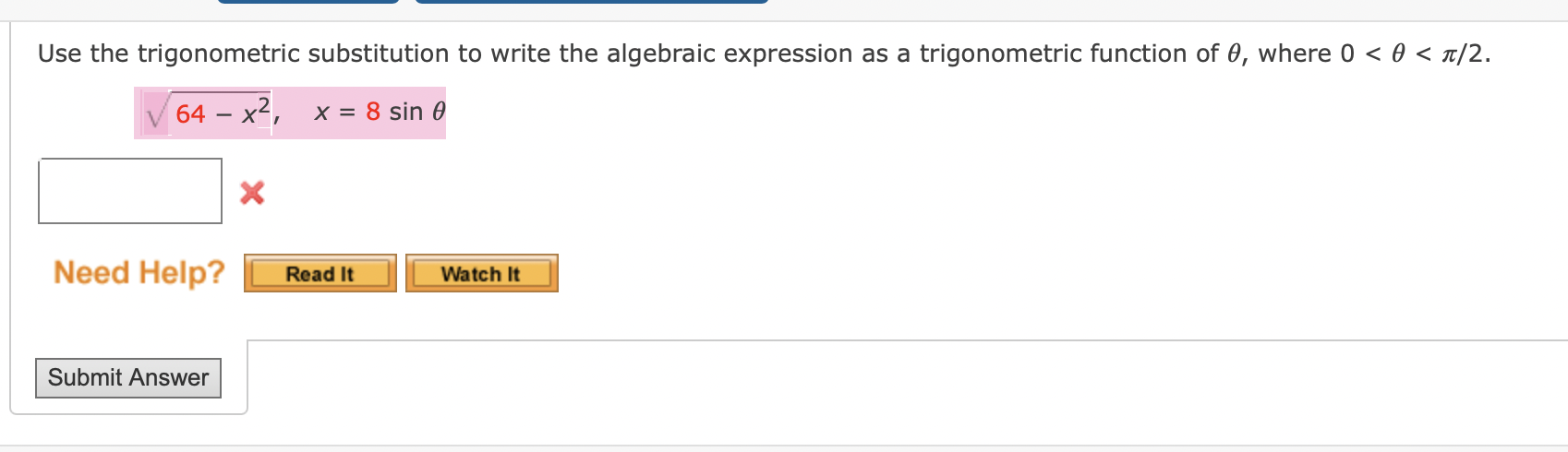



11 Use The Trigonometric Substitution To Write The Chegg Com
The given trigonometric equation can be proven by using the appropriate algebraic manipulations and Trigonometric identities as follows (sin x cos x 1) (sin x cos x ‒ 1) = sin 2x After performing the indicated multiplication shown on the left and adding the partial products, we have the following productI want to know how to solve these kind of problems so please don't just show me the answer(2)圖解正餘弦函數的疊合: DFDE=asinxbcosx CG=AC⋅sin(xθ),其中AC= a2b2 ,而tanθ =b a B因為DFDE=CG 所以asinxbcosx= a2b2 sin(xθ) 結論: (1)可將正餘弦函數的線性組合asinxbcosx 化成正弦函數,也可化成餘弦函數。 (2)− a2b2≤ y=a⋅sinxb⋅cosx≤ a2b2 (3) f(x)=a⋅sinxb⋅cosx 的週期為2π 。 A F D C E



Pplato Flap Math 3 3 Demoivre S Theorem And Complex Algebra




81 X Dx Example 1 Evaluate X2 Solution Let X 9 Chegg Com
sinθ=青/赤、cos (θπ/2)=緑/赤 青=緑 ∴sinθ=cos (θπ/2) 右の図 cosθ=緑/赤、sin (θπ/2)=緑/赤 緑=青 ∴cosθ=sin (θπ/2) 9 件Free trigonometric equation calculator solve trigonometric equations stepbystep Trigonometric Identities (1) Conditional trigonometrical identities We have certain trigonometric identities Like sin2 θ cos2 θ = 1 and 1 tan2 θ = sec2 θ etc Such identities are identities in the sense that they hold for all value of the angles which satisfy the given condition among them and they are called




Trigonometry Addition Formula For Rcos X A And R X A Ppt Download
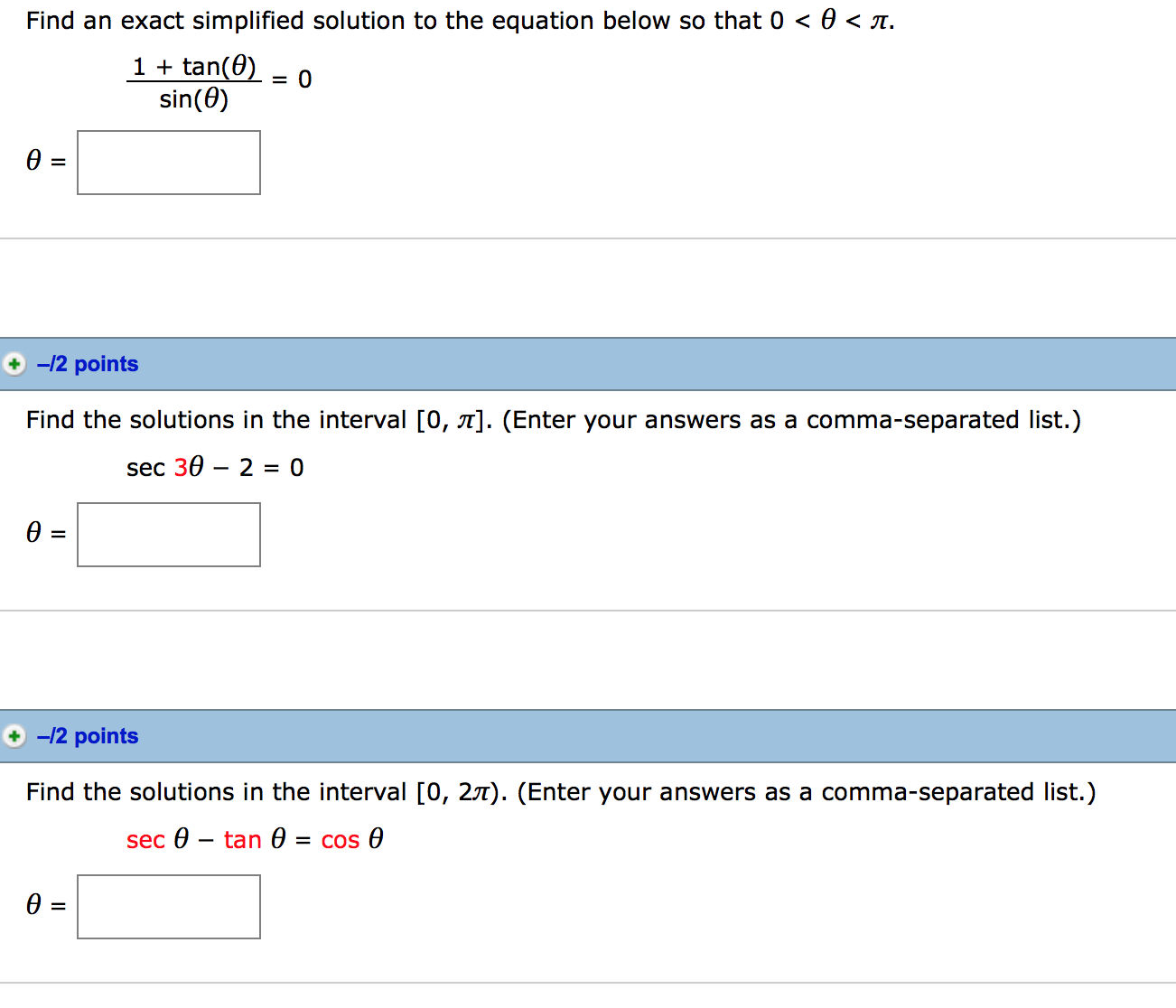



Find An Exact Simplified Solution To The Equation Chegg Com
θ = y x で表される3つの三角比の関数のことを、 三角関数 と言います。 「 sin θ, cos θ, tan θ の分母・分子をド忘れしそう」と感じる方も多いかもしれませんが、これらはその 頭文字 s,c,t の筆記体 のイメージと結びつけると覚えやすくなりGiven `sin theta cos theta = sqrt(2)cos theta` prove `cos theta sin theta = sqrt(2)sin theta` `sin theta cos theta = sqrt(2)cos theta` square both sidesTo remember the trigonometric values given in the above table, follow the below steps First divide the numbers 0,1,2,3, and 4 by 4 and then take the positive roots of all those numbers Hence, we get the values for sine ratios,ie, 0, ½, 1/√2, √3/2, and 1 for angles 0°, 30°, 45°, 60° and 90°




If Sintheta Costheta Sqrt 2 Costheta Then The General Value Of Theta Is




10 Polar Coordinates Parametric Equations Pdf Free Download
Sin(θ π 2) = cosθ sin(θ π) = −sinθ sin(θ 2π) = sinθ cos(θ π 2) = −sinθ cos(θ π) = −cosθ cos(θ 2π) = cosθ tan(θ π 2) = −(tanθ)−1 tan(θ π) = tanθ tan(θ 2π) = tanθ Les fonctions sinus et cosinus sont p´eriodiques, de p´eriode 2π La fonction tangente est p´eriodique, de p´eriode πSolve your math problems using our free math solver with stepbystep solutions Our math solver supports basic math, prealgebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and moreFind Study Resources by School by Literature Title Study Guides




Part Iii Given Sin 8 1 2 And Frac P 2 Gauthmath
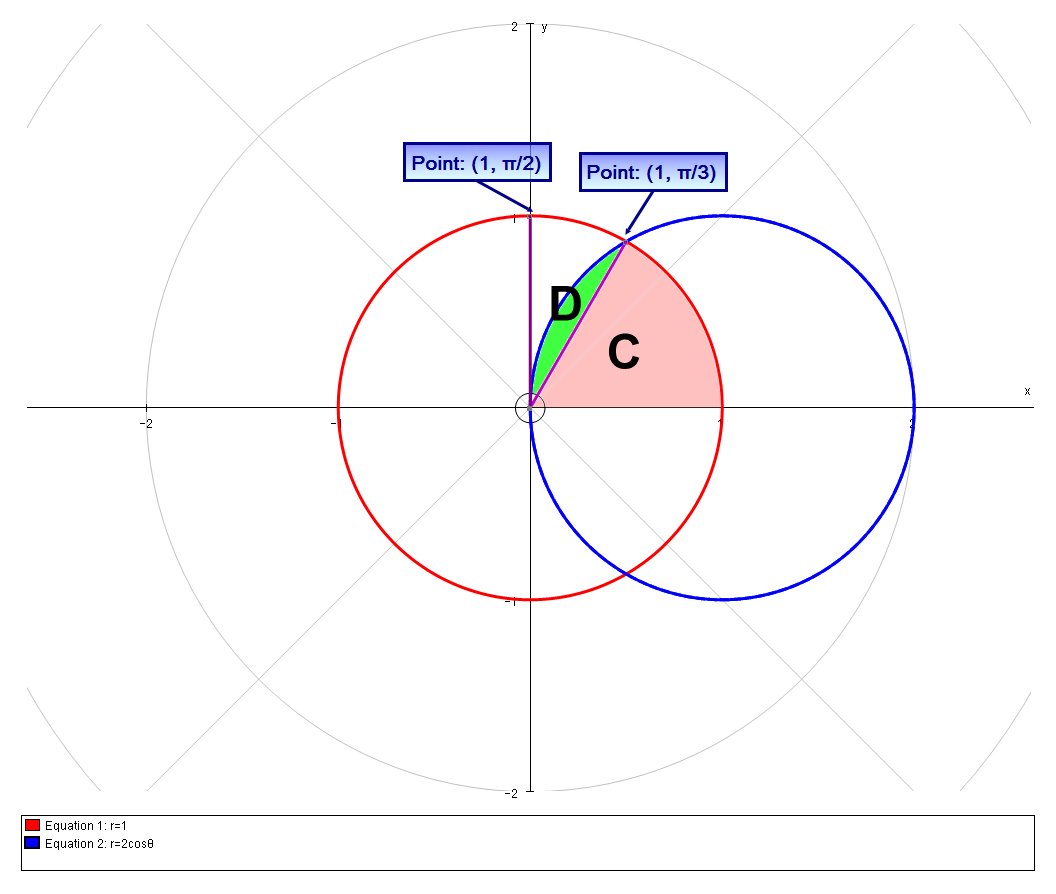



What Is The Area Inside The Polar Curve R 1 But Outside The Polar Curve R 2costheta Socratic
π/2−θの三角関数の公式 これらの公式を利用して、次の公式を証明してみましょう。 公式の証明は加法定理を用いておこなうこともできますが、今回は加法定理を学習していなくてもできる方法で行います。 sin(π/2−θ)=cosθView Chapter_07_part_2_slidespdf from MATH 1131 at Ali Law College MATH1131 Calculus Chapter 7 Curve sketching Part 2 Polar curves 1 Polar coordinates r>0 P (r,θ) θ O Points in the planeSin(θ) = sin θ Even and Odd What happens when you change the sign of θ (cos(πθ), sin(πθ)) (cosθ, sinθ) πθ θ cos(πθ) = cos(θ);




If X A Cos 28 28 Sin 28 And Y A Sin 28 28 Cos 28 Find
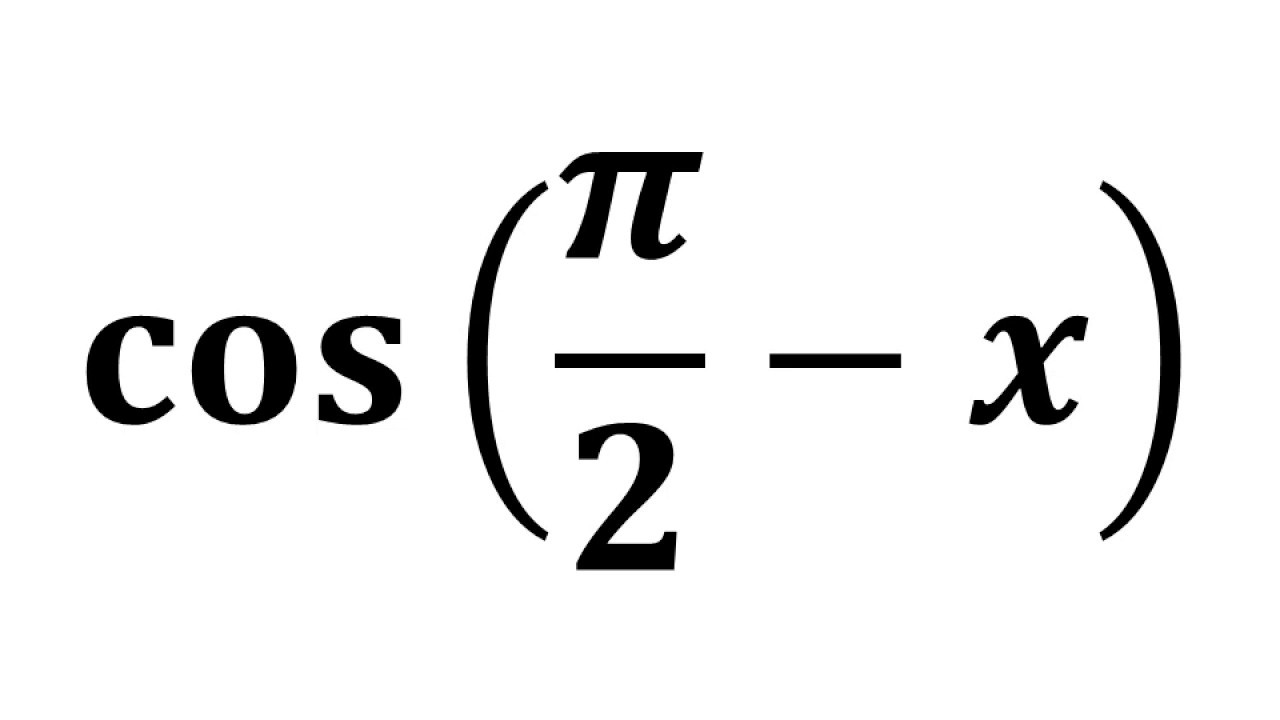



Cot Pi 2 X Cot Pi 2 Theta Youtube
(cosθ, sinθ) (cos(θ), sin(θ))θ θ cos(θ) = cosθ;The easiest way is to see that cos 2φ = cos²φ sin²φ = 2 cos²φ 1 or 1 2sin²φ by the cosine double angle formula and the Pythagorean identity Now substitute 2φ = θ into those last two equations and solve for sin θ/2 and cos θ/2 三角関数で sinθ=cos(θπ/2) と sinθ=cos(π/2θ) の2つの公式があるのですが、 なぜ、cosのθとπ/2 を入れ替えてもどちらもsinθになるのですか? 高校数学



Pplato Flap Math 1 6 Trigonometric Functions




7 If Cos Theta Frac 12 13 0 Theta Frac Pi 2 Find The Value Of Sin 2 Theta Cos 2 Theta Frac Sin 2 Theta Cos 2 Theta 2 Sin Theta Cos Theta Cdot Frac 1
A Computer Science portal for geeks It contains well written, well thought and well explained computer science and programming articles, quizzes and practice/competitive programming/company interview QuestionsHow to find Sin Cos Tan Values?ID A 1 T Unit 12 Intro to Trigonometry Review Answer Section MULTIPLE CHOICE 1 ANS C If cscP > 0, sinP > 0 If cotP < 0 and sinP > 0, cosP < 0 PTS 2 REF 0613a2 STA A60 TOP Finding the Terminal Side of an Angle
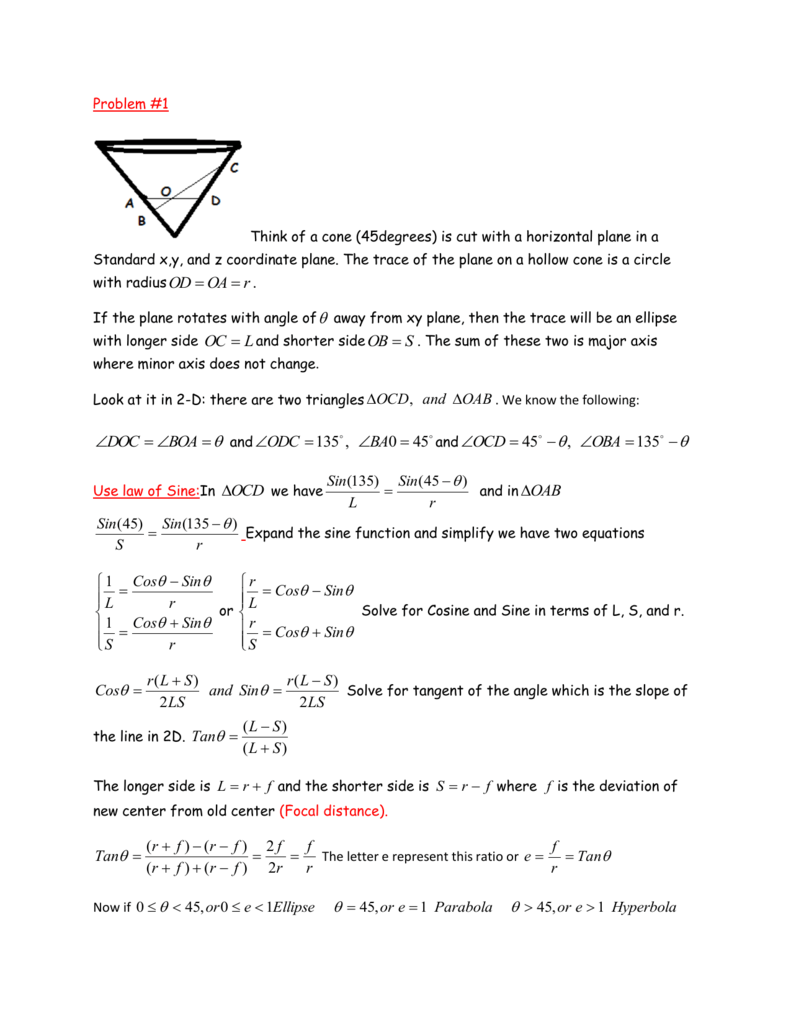



Problem 1 Think Of A Cone 45degrees Is Cut With A Horizontal




Given That Sin Theta 1 4 0 Theta P 2 What What Is The Exact Value Of Cos 8 Brainly Com
Sin(πθ) = sin(θ) Supplementary angles θ (cosθ, sinθ) θ This figure defines sine and cosine It helps you remember whenShift by π/2 shift by π shift by 2π sin(θπ/2) = cosθ sin(θπ) = sinθ sin(θ2π) = sinθ cos(θπ/2) = sinθ cos(θπ) = cosθ cos(θ2πIn one cycle Notice the roots for dx dθ and dy dθ do not overlap When the tangent is horizontal, dy dx = 0, ie when dy dθ = 0, but dx dθ 6= 0, then we get θ= π/2,3π/2 in one cycle




Frac Sin 8 P Cot 8 Frac 7 P 2 Sec 8 Gauthmath




If Cos8 12 13 0 Lt 8 Lt P 2 Find The Value Of Sin2 8 Cos2 8 2 Sin 8 Cos 8 1 Tan2 8 Brainly In
定理です。 sin(αβ)=sinα×cosβcosα×sinα という公式が成り立っています。α=θ β=π/2 として計算してみてください。 後、θ cos (πθ)について、π回転するとラベルはcosなので、まず cos (θ)になります。 そして、cos (θ)=cosθは暗記しておいて、cos (θ)=cosθとします。 これで、cos (πθ)=cosθが得られました。 丁寧に解説して下さってありがとうございます。 おかげでSin(θ) = sinθ cos(θ) = cosθ tan(θ) = tanθ Some Useful Relationships Among Trigonometric Functions sin2θ cos2θ = 1 sec2θ – tan2θ = 1 csc2θ – cot2θ = 1 Double Angle Formulas sin2θ = 2 sinθ cosθ cos2θ = cos2θ – sin2θ = 12 sin2θ = 2 cos2θ




Proved That 2 Sin P 4 Theta Costheta Sintheta Brainly In




How To Find The General Solution Of Sin Left Theta Frac Pi 6 Right Cos 3 Theta Mathematics Stack Exchange
176 A MerryGoRound revolves 2 times per minute, Jack is 10 feet from the center while Bob is 14 feet from the center Jack's linear speed is ___ ft per min Bob's linear speed is ___ ft per min pi/12 803 Allison lives in Kansas City, which has coordinates of 39°5'59" N, 94°34'41 W (° N, 9457° W) (Earth's radius is 3950 miles)The solutions are θ = π 2, 3π 2 and θ = 2π 3, 4π 3 7 Solve 2sin2 θ −sinθ −1 = 0 on the interval 0 ≤ θ < 2π 2sin2 θ −sinθ −1 = 0 (2sinθ 1)(sinθ −1) = 0 ⇒ sinθ = − 1 2, sinθ = 1 The solutions are θ = 7π 6, 11π 6 and θ = π 2 13 Solve sin2 θ = 6(cosθ 1) on the interval 0 ≤ θ < 2π sin2 θ = 6(cosθQuestion Find the exact values of sin 2θ, cos 2θ, and tan 2θ for the given value of θ cos θ = 3/5;
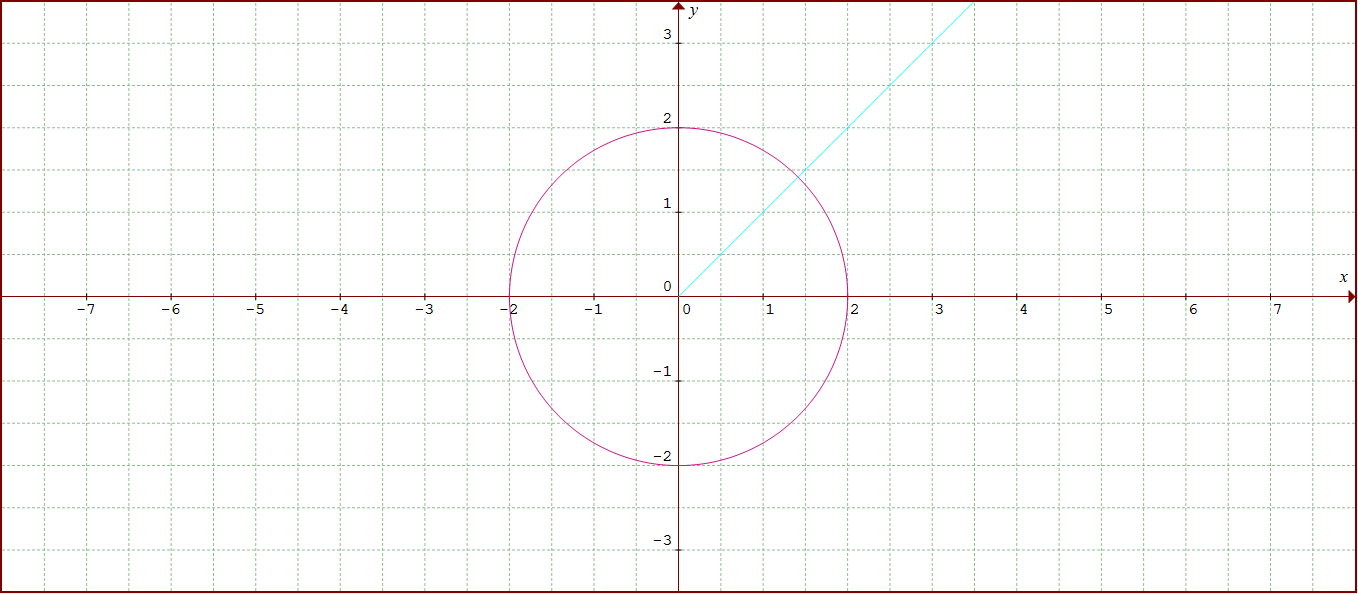



How Do You Find The Points Of Intersection Of Theta Pi 4 R 2 Socratic




Use The Trigonometric Substitution To Write The Chegg Com
In our case, for example, we have two oscillators with a phase difference equal to π/2 and, hence, Δ would be 0 for one oscillator, and –π/2 for the other The formula to apply here is sinθ = cos(θ – π/2) Also note that we can equate our θ argument to ω 0 ·t Now, if a = 1 (which is the case here), then these formulas simplify to04 Exponential and Trigonometric Functions 48 Theorem 022 Natural ExponentialFunctions Every exponential function can be written in the form f(x)=Aekx for some real number ANote that if two angles add up to 90 , they are called " complimentary angles " If two angles add up to 90 or π / 2, the sine of one is equal to the cosine of the other Also, the tangent of one is equal to the cotangent of the other θ and (π / 2 θ) are complimentary angles because θ (π / 2




T E A Cos Theta Sin Theta Tuer Sin Theta Quad Cos Theta 0 Frac 1 2 Frac 1 Sqrt 2 Frac Sqrt 3 2 Frac 1 Sqrt 2 The Matin A When Theta Pi
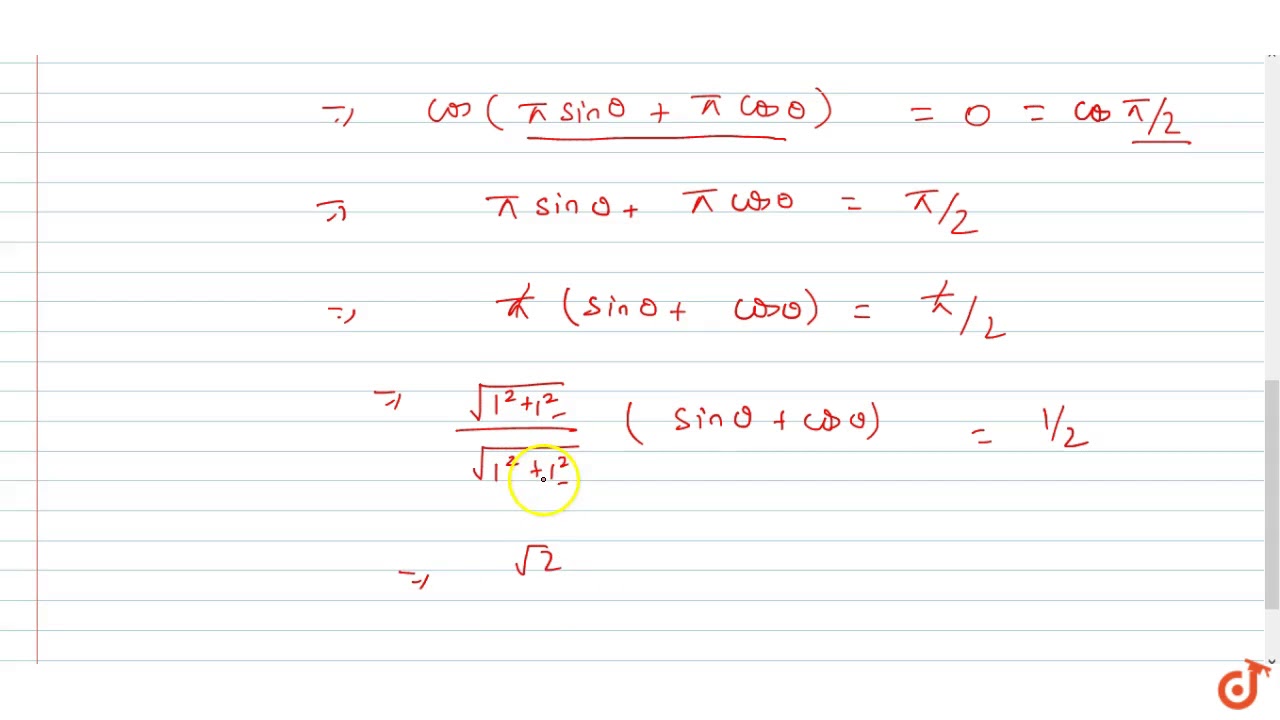



If Tan Pi Cos Theta Cot Pi Sin Theta Then Prove Cos Theta Pi 4 1 2 Sqrt2 Youtube
Sinθ = 12/13 (opp/hyp) (12)^2 x^2 = (13)^2 x^2 = 169 144 x^2 = 25 x = 5 Cosθ = 5/13 (adj/hyp) Cosθ Sinθ = 5/13 12/13 = 17/13 =Sin(θ 2π) = sinθ cos(θ 2π) = cosθ tan(θ π) = tanθ csc(θ 2π) = cscθ sec(θ 2π) = sec cot(θ π) = cotθ That is, the functions sinθ, cosθ, cscθ, and secθ have period 2π, and functions tanθ and cotθ have period π Examples Page 367 numbers 14 and 24 Note We can also determine the sign for each trigonometric function by0° θ 90° a)sin 2θ b)cos 2θ c)tan 2θ Please help!




Math Polar Coordinates Ppt Download




Question Video Finding The Slope Of The Tangent To A Polar Curve At A Given Point Nagwa
Find the max and min values of f(θ) = sin^2(sinθ) cos^2(cosθ) asked in Differential equations by Raghab ( 505k points) differential calculus




Iii Frac Sin 8 P Cos Tfrac 7 P 2 Sec Gauthmath



What Is The Equation Of The Tangent Line Of R Cos 2 Theta Pi Sin 2 Theta 3pi Theta At Theta 13pi 4 Socratic
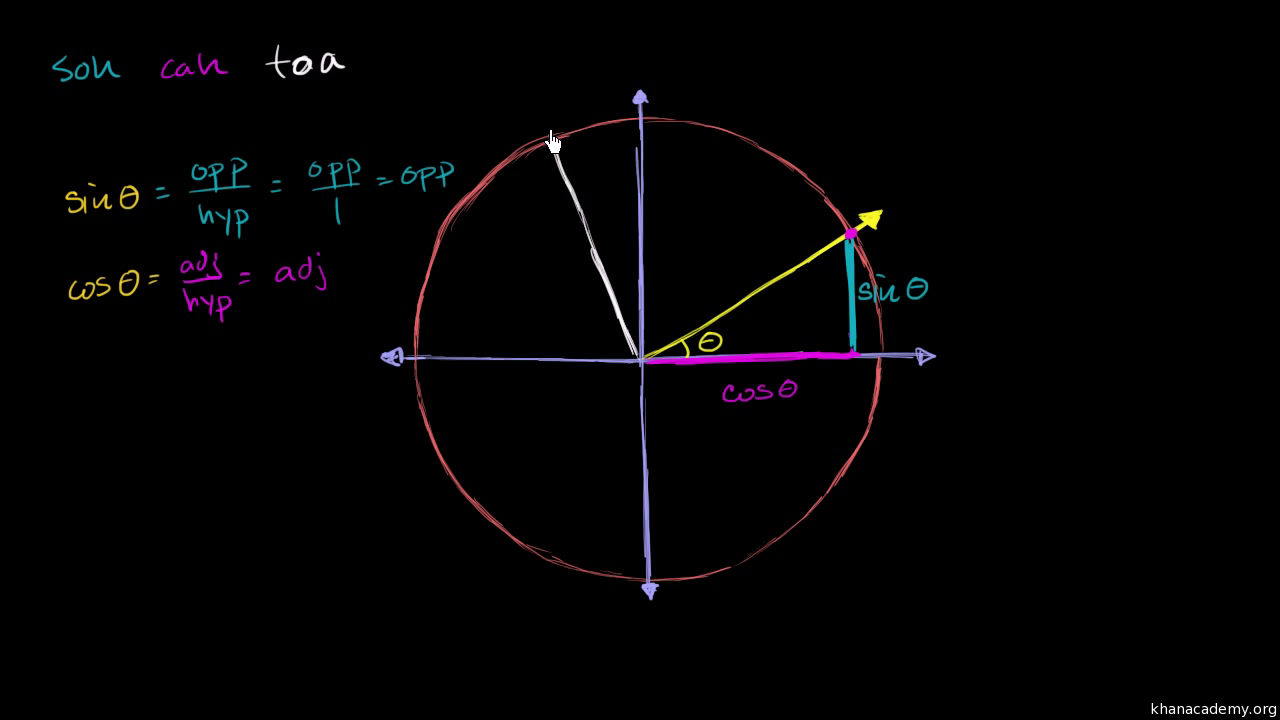



Sine Cosine Identities Periodicity Video Khan Academy




4 If Sin 8 5 13 And Frac P 2 8 P Gauthmath




Trigonometric Functions Wikipedia
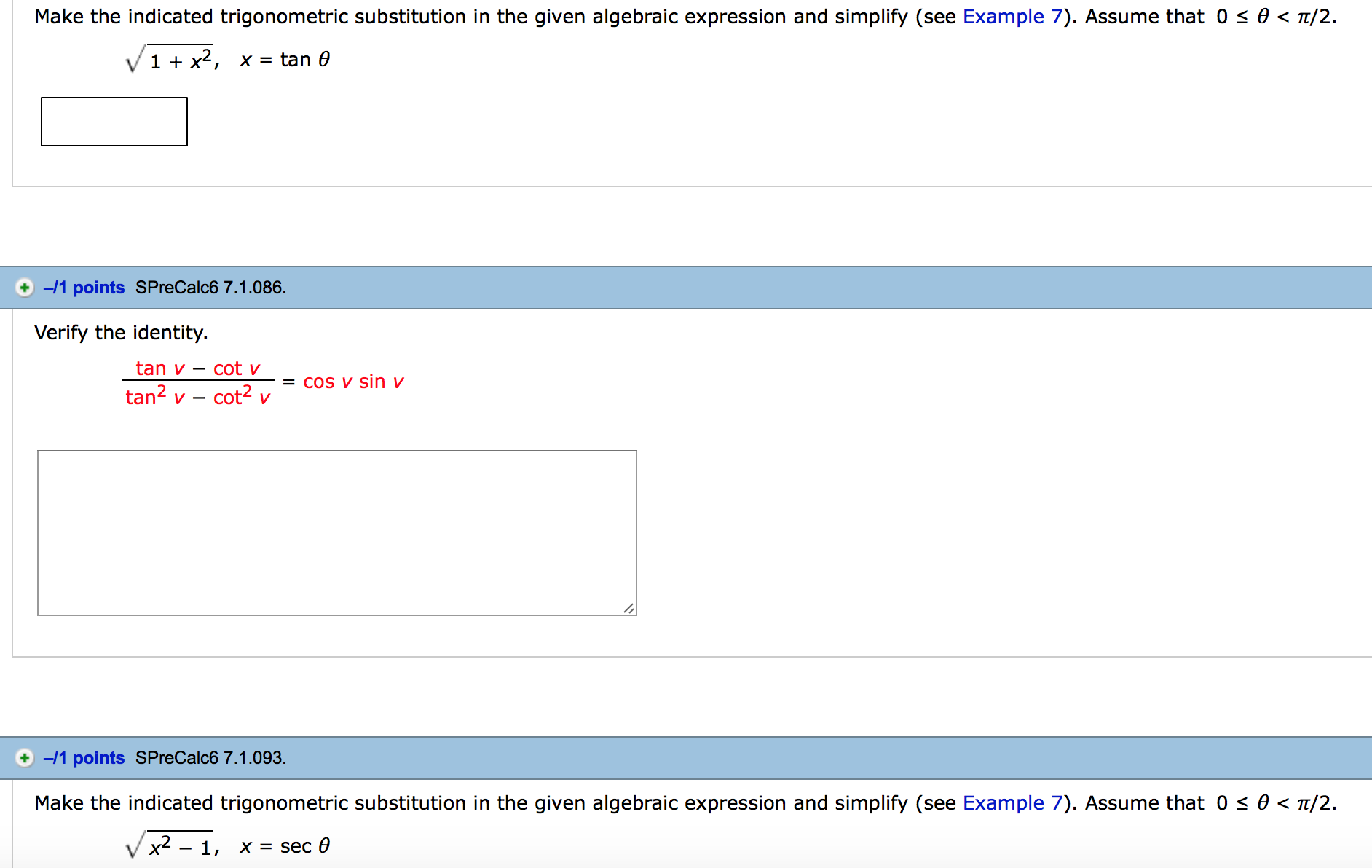



Make The Indicated Trigonometric Substitution In The Chegg Com



1




Trigonometry Addition Formula For Rcos X A And R X A Ppt Download




2 Given That Cos 8 3 5 Find That 8 Is Gauthmath
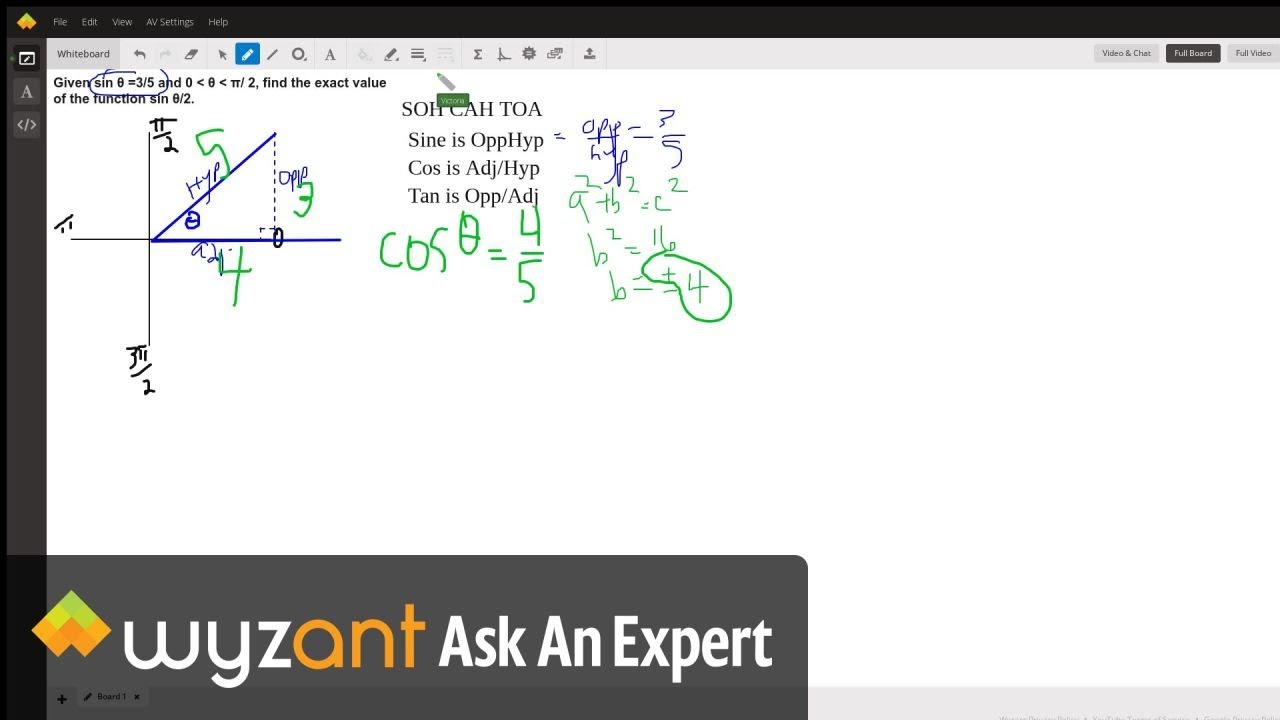



Given Sin 8 3 5 And 0 8 P 2 Find The Exact Value Of The Function Sin 8 2 Wyzant Ask An Expert




Use The Unit Circle To Evaluate The Six Trigonometric Functions Of 8 P Sin 8 Cos 8 Tan 8 Csc Brainly Com
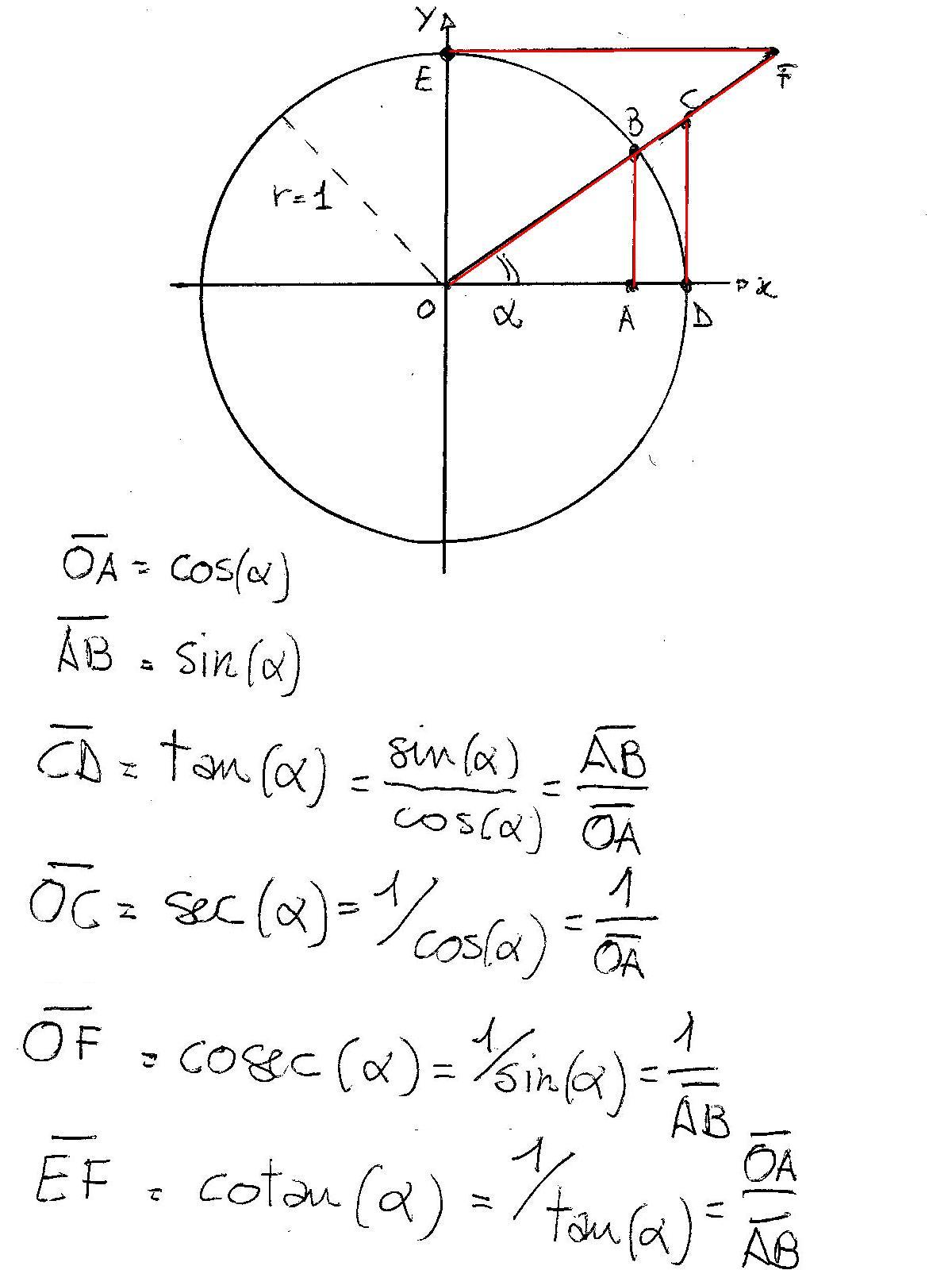



Basic Trigonometric Functions Trigonometry Socratic




A Animation Of Symmetric Transformations Left And Right Plot Denotes Download Scientific Diagram



Pplato Flap Math 1 6 Trigonometric Functions




Find The Length Of Normal To The Curve X A Theta Sintheta Y A 1 Costheta At Theta Pi 2dot
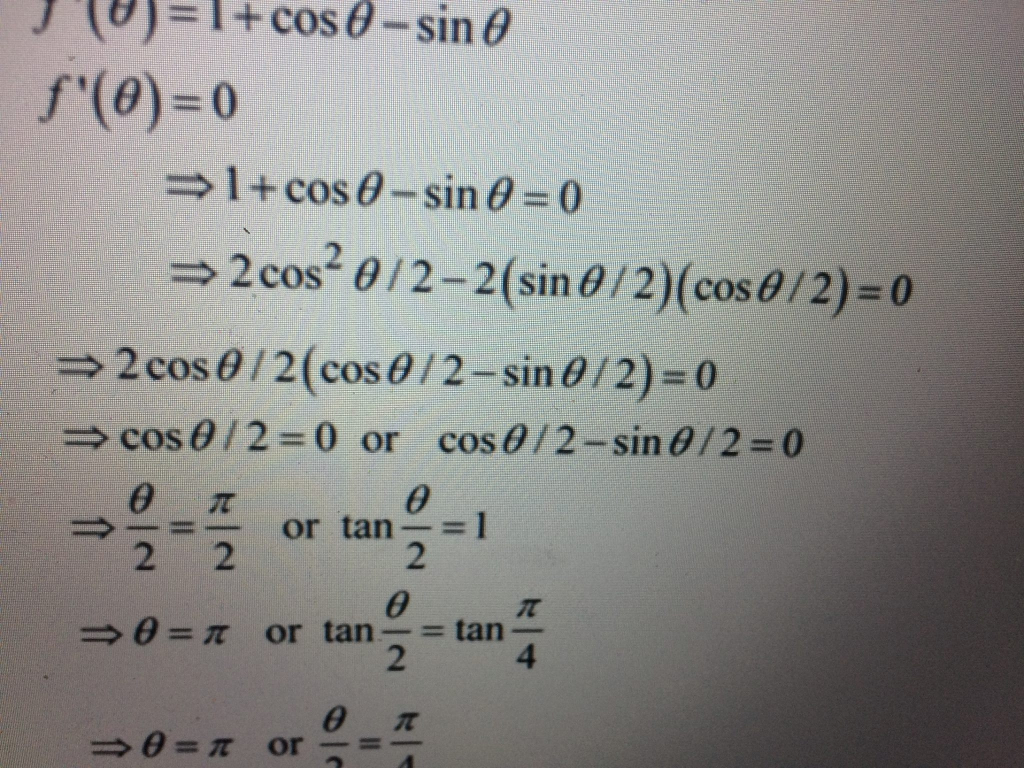



F Theta 0 1 Cos Theta Sin Theta 0 2 Cos 2 Chegg Com
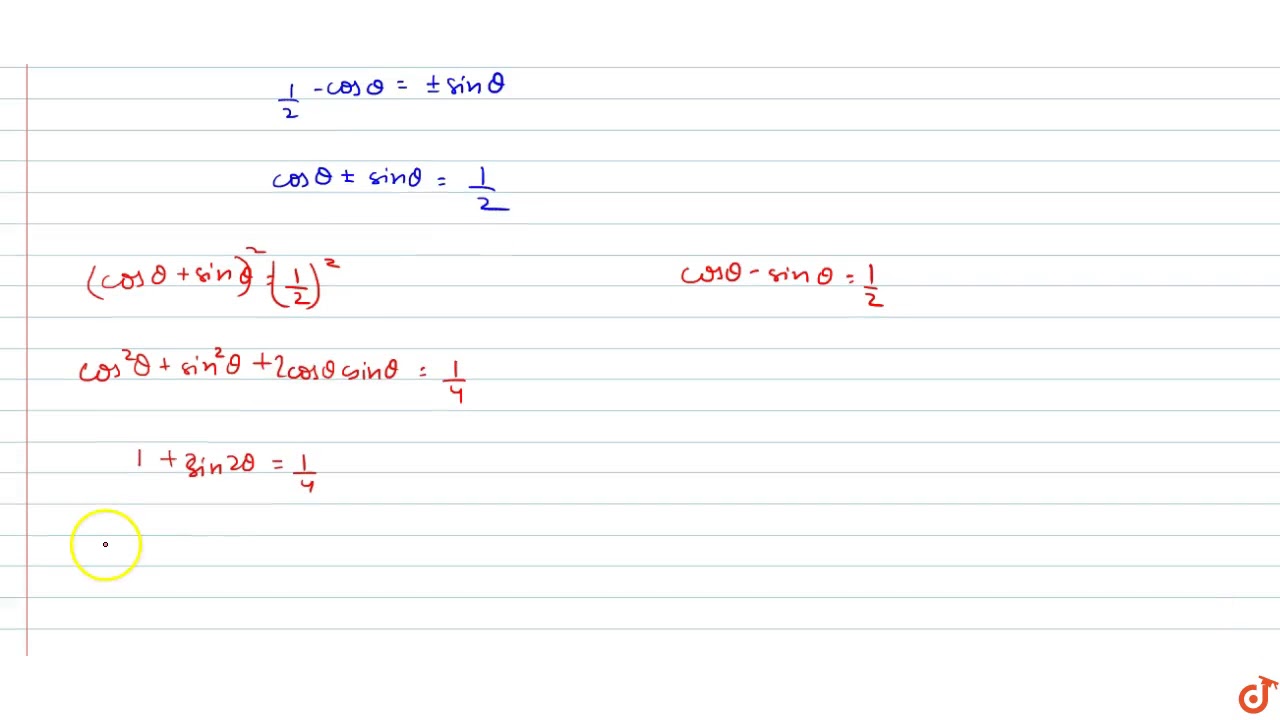



If Sin Pi Cos Theta Cos Pi Sin Theta Then Sin 2theta Youtube




If 2 Cos Theta Sin Theta 1 Theta Pi 2 Then 7 Cos Theta 6 Sin Theta Is Equal To Youtube
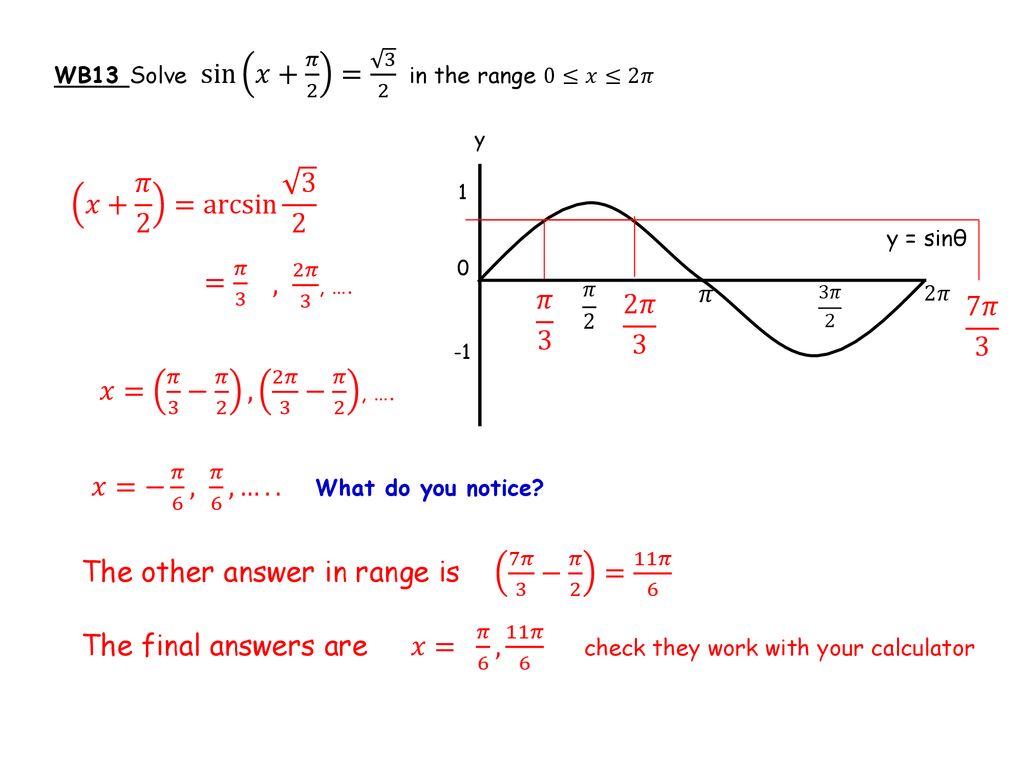



Trig Graphs And Equations Ppt Download




List Of Trigonometric Identities Wikipedia



Solving Cos 8 1 And Cos 8 1 Video Khan Academy



Solved Consider The Function F 6 6coszb 65in6 A Find F 6 12 Cos 0 Sin 0 6 003 0 V B Determine The Critical Points Of Fw On The Course Hero




Lim Theta Pi 2 1 S Intheta Pi 2 Theta Costheta Is Equal To A 1 B 1 C 1 2 D 1 2




Let Theta Frac Pi 5 X Left Begin Array




13 Let A Left Theta 2 Cos 2 Theta Sin Theta Leq 2 Right And B Theta Pi 2 Leq Theta Leq 3 Pi 2 Find A Cap B




Find The Exact Values Of Sin 28 Cos 28 And Tan 28 Given The Following Sin 8 12 13 Where 8 Is In Quadrant Iv Wyzant Ask An Expert
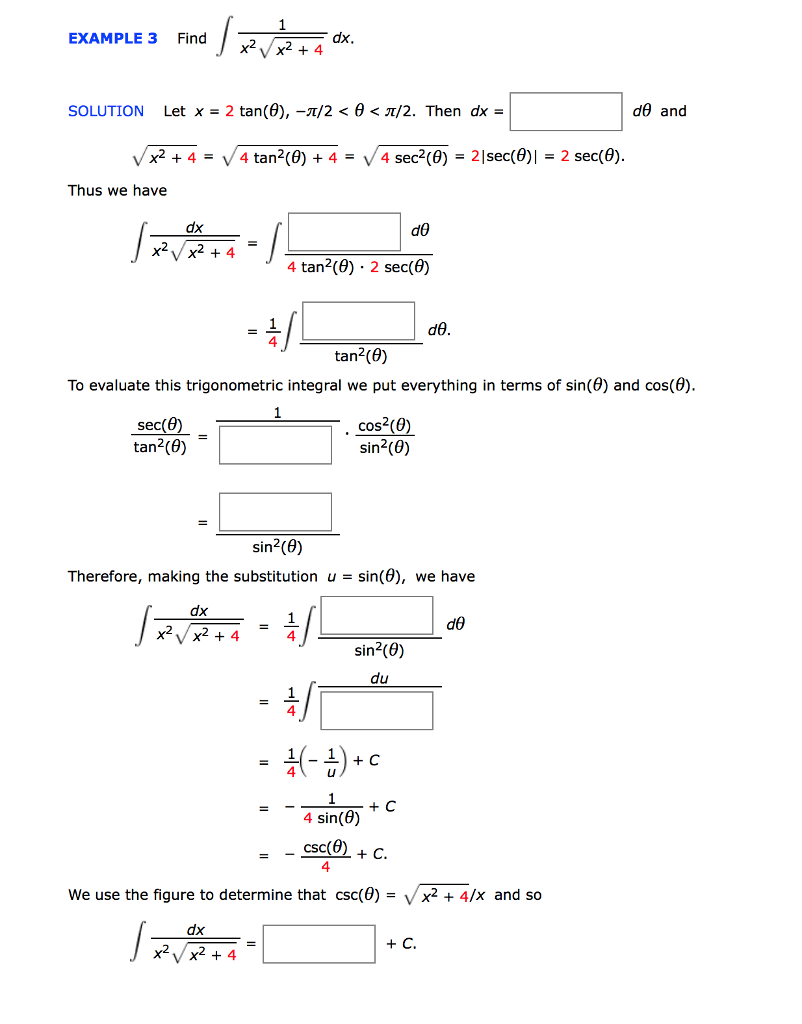



Example 3 Find Dx Solution Let X 2 Tan 8 Z 2 Chegg Com




Is The Function F X Cos X Even Odd Or Neither Socratic



1




Limit Examples 1 Lim 8 Csc 8 Lim 8 Sin 8 1 Lim Sin 8 8 1 1 1



Http Www Southampton Ac Uk Cjg Eng1 Modules Old 07mod2 Pdf




Math Polar Coordinates Ppt Download




Example 1 Evaluate X2 Solution Let X 9 Sin 8 Where Chegg Com




Find The Equation Of The Tangent To The Curve X Theta Sin Theta Y 1 Cos Theta At Theta Pi Youtube




Prove That Sin Theta Pi 6 Cos Theta Pi 3 Sqrt3 Sintheta Youtube



Web Auburn Edu Holmerr 1617 Textbook Trigonometry Print Pdf




Ex 6 2 9 Prove That Y 4 Sin 2 Cos Theta Is Increasing




Polar Curves Intersections Ppt Download



Q Tbn And9gcrhjnlyw8wv0cglkfihjo Yekht4szwsqxuapexkgb Lljycs L Usqp Cau




If Sin Theta 4 5 And Pi Lt Theta Lt 3pi 2 Find The Values Of All The Other Five Trigonometric Functions




If X Theta Sin Theta Y 1 Cos Theta Then At Theta Pi 2 Dy Dx Youtube




7 4 Double Angle And Half Angle Identities Ppt Download




Using The Pythagorean Trig Identity Video Khan Academy




Trigonometric Functions Of Allied Angles Sin Pi Theta Sin Theta Cos Pi Theta Cos Theta Tan Pi Theta Tan Theta Sin 2 Pi Theta Sin Theta Cos 2 Pi Theta Cos Theta Tan 2 Pi Theta Tan Theta Sin Left Frac 3
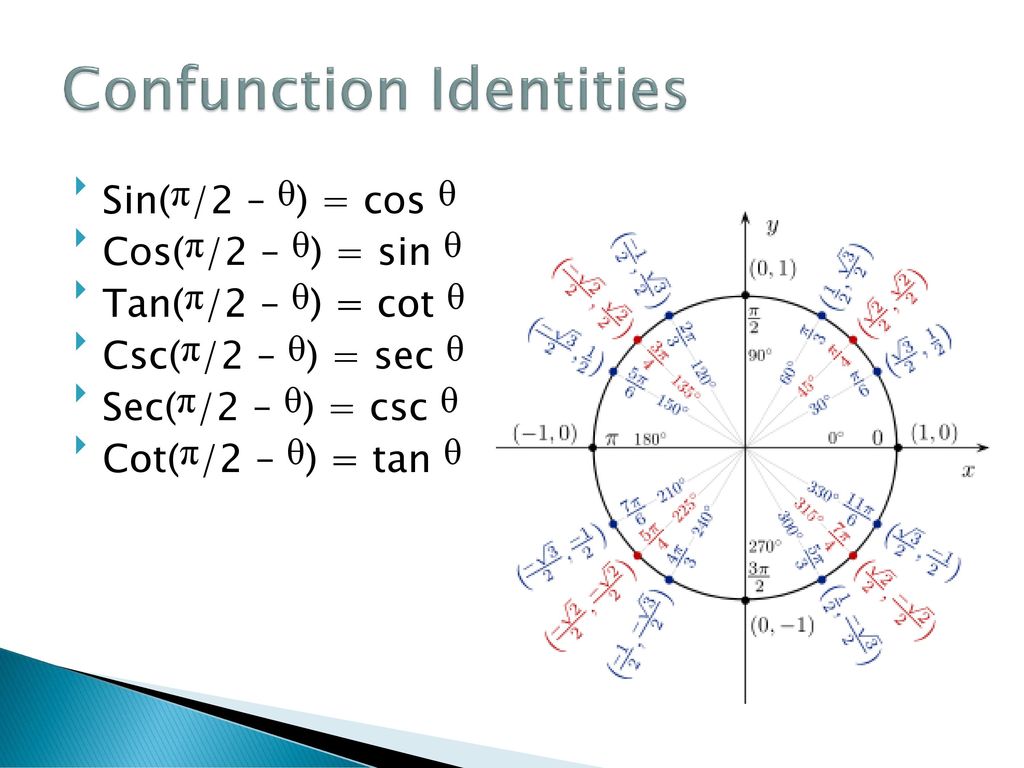



Chapter 5 Analytic Trigonometry 5 1 Fundamental Identities Ppt Download




How Can The Maximum Value Of F Theta 5 Cos Theta 3 Cos Theta Pi 3 Be 10 Mathematics Stack Exchange




Find The Volume Bounded Above The Sphere R 2a Cos Theta And Below The Cone Phi Alpha Where 0 Alpha Frac Pi 2 Mathematics Stack Exchange




For All Theta In 0 Pi 2 Show That Cos Sintheta Sin Costheta



Http Www Webassign Net Latex2pdf 3ddbde5ac156fd5 Pdf




Sin 8 Sin 58 Sin 38 And 0 Lt 8 Lt P 2 Then What Is The Value Of 8 In Degrees Brainly In



1
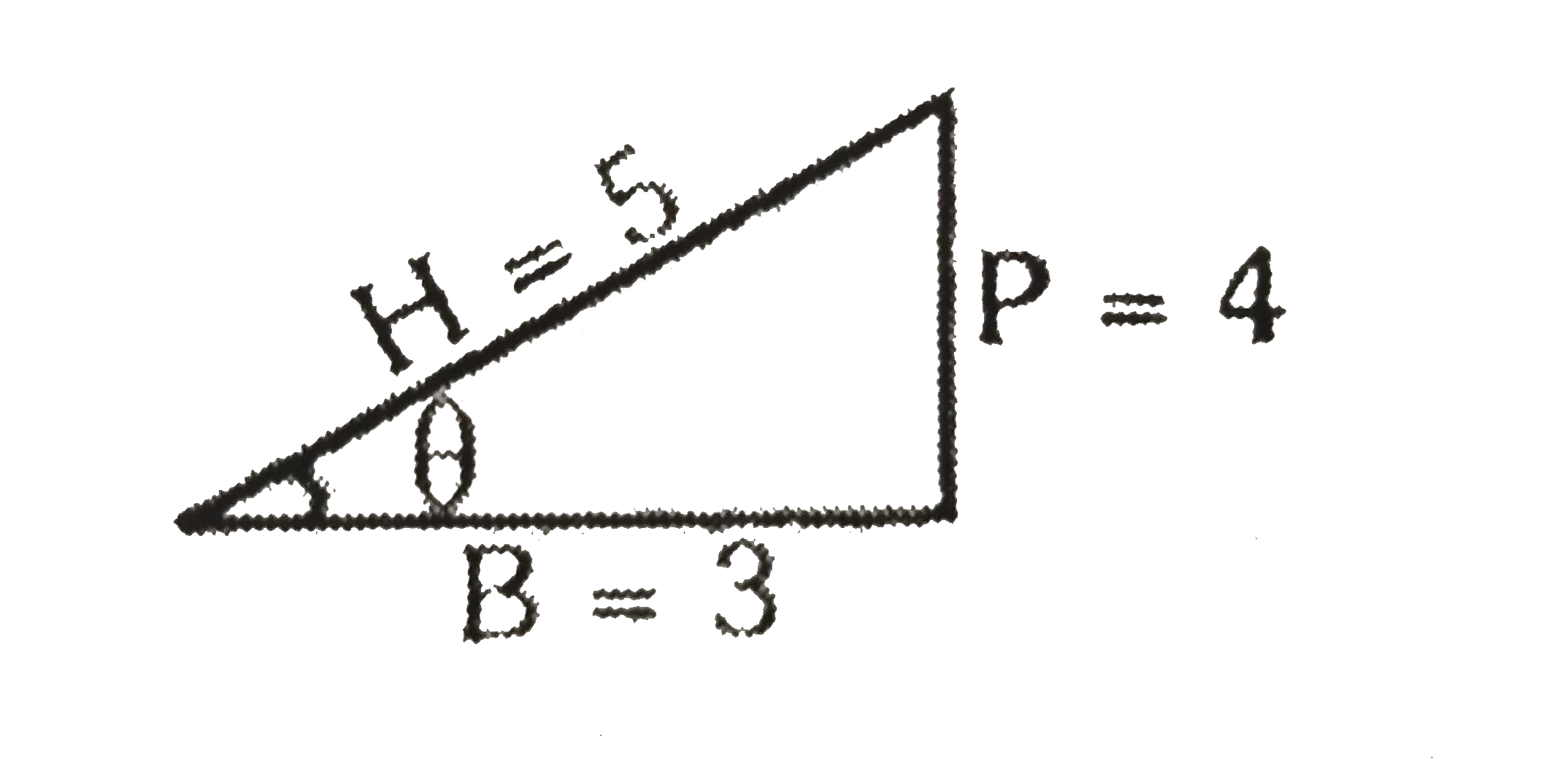



If Sec Theta 5 3 And 0 Lt Theta Lt Pi 2 Find All T



Www Cerritos Edu Dford Sitepages Math 140 Math140lecture15 Pdf



Sin 28 2sin 8 Cos 8 Proof Video Dailymotion
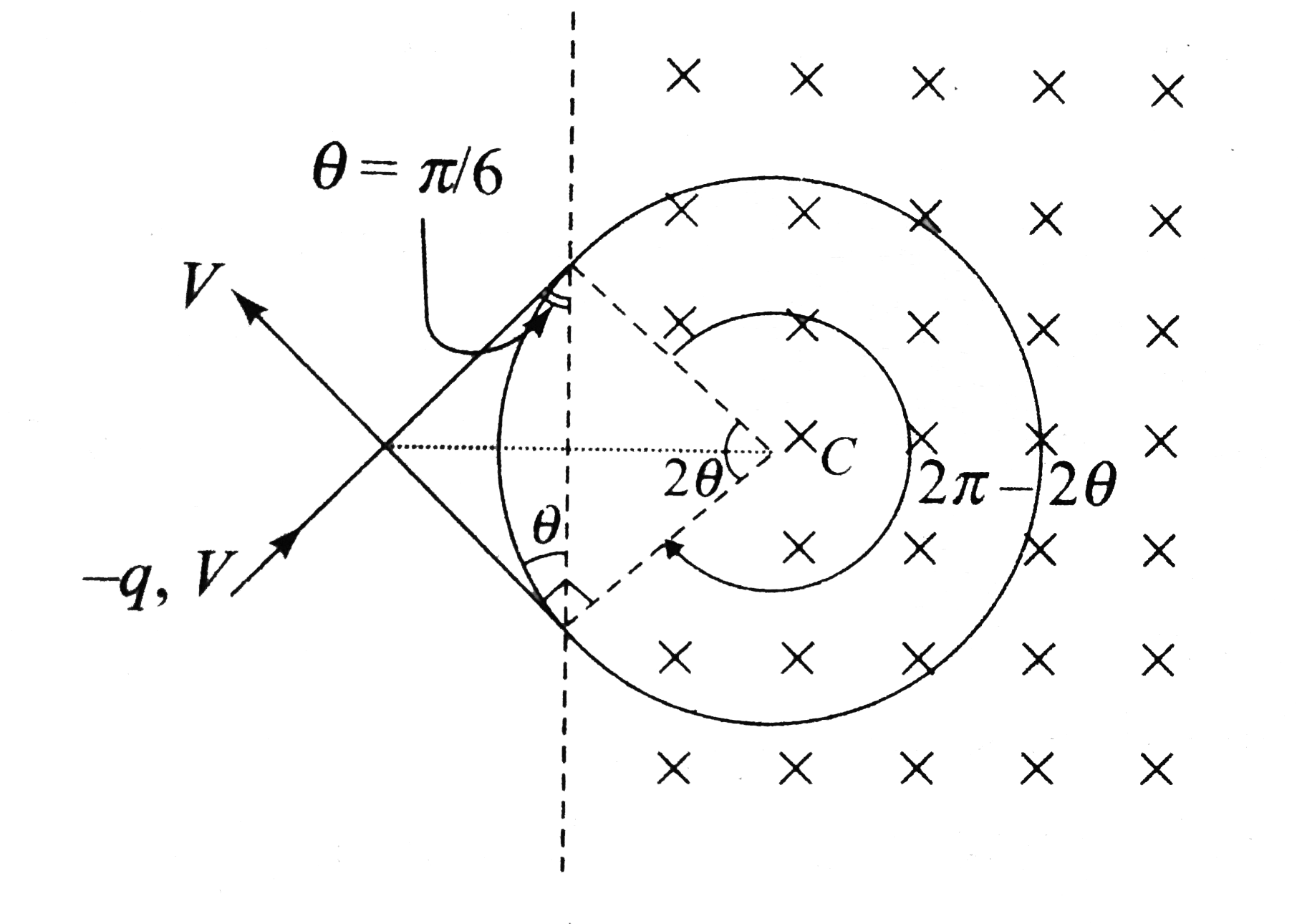



Repeat Above Question 3 If The Charge Is Negative And The Angl




Given That Tan 8 3 7 And Frac P 2 8 Gauthmath
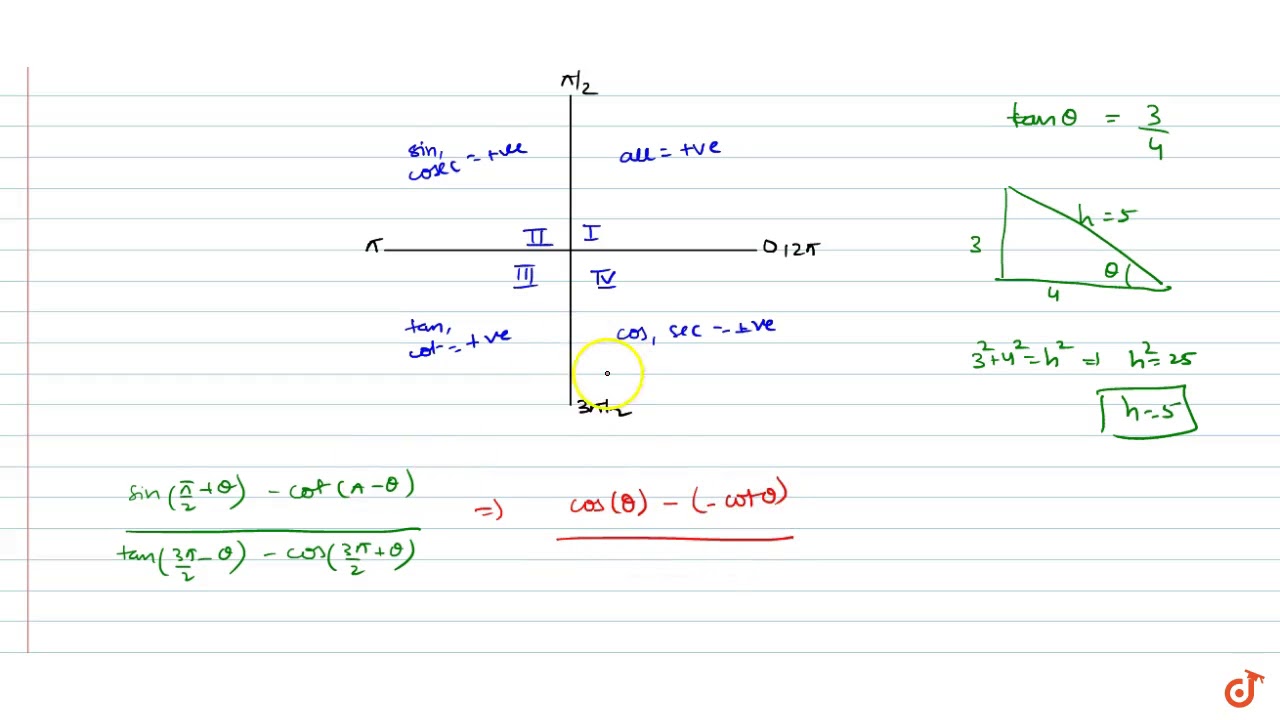



If Tan Theta 3 4 And Theta Is Not In First Quadrant Then Sin Pi 2 Theta Cot Pi Theta Youtube
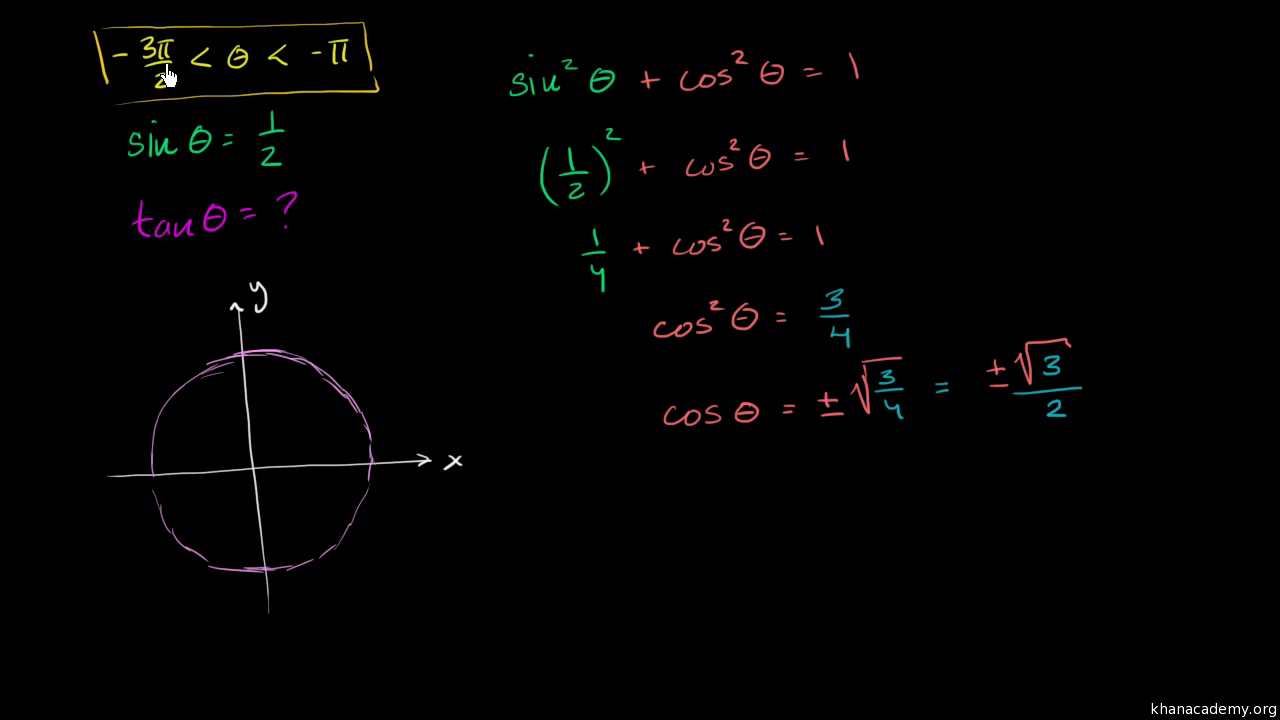



Using The Pythagorean Trig Identity Video Khan Academy




Given Sin 8 3 5 And 0 8 P 2 Find The Exact Value Of The Function Sin 8 2 Wyzant Ask An Expert




Variation Of A S 8 R 0 8 Cos ϕ And B S ϕ R 0 8 Sin ϕ Download Scientific Diagram
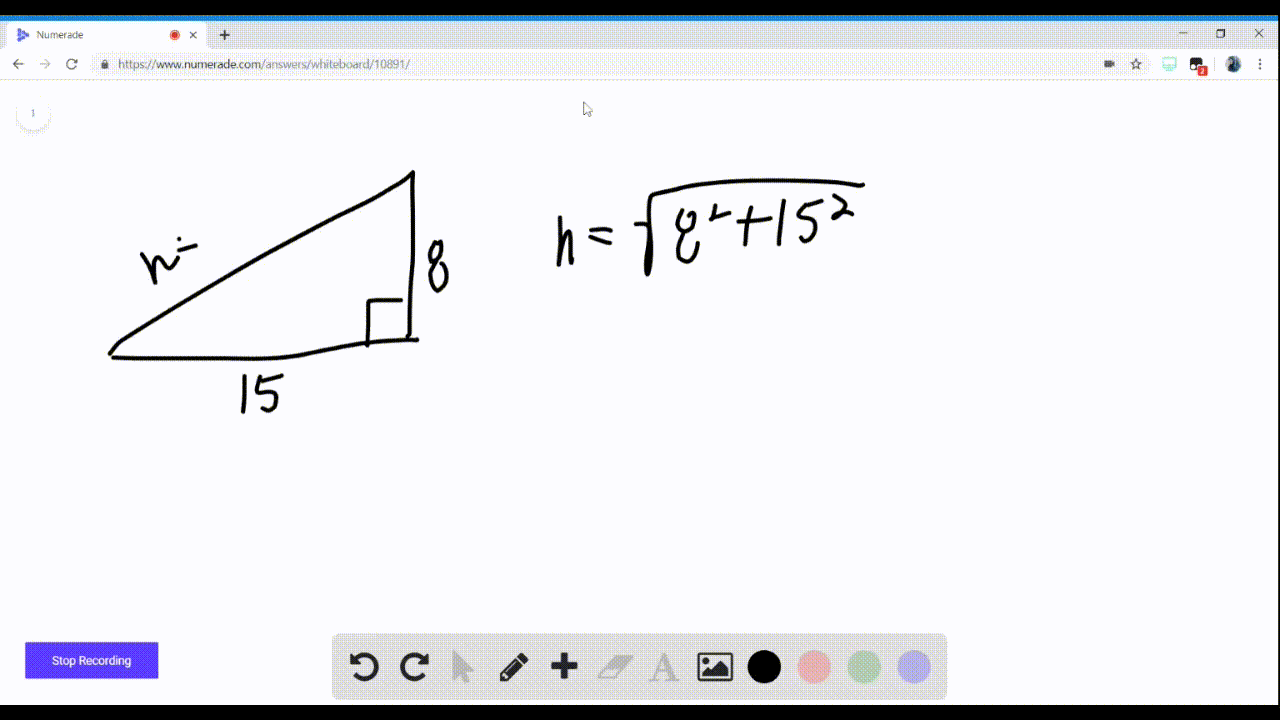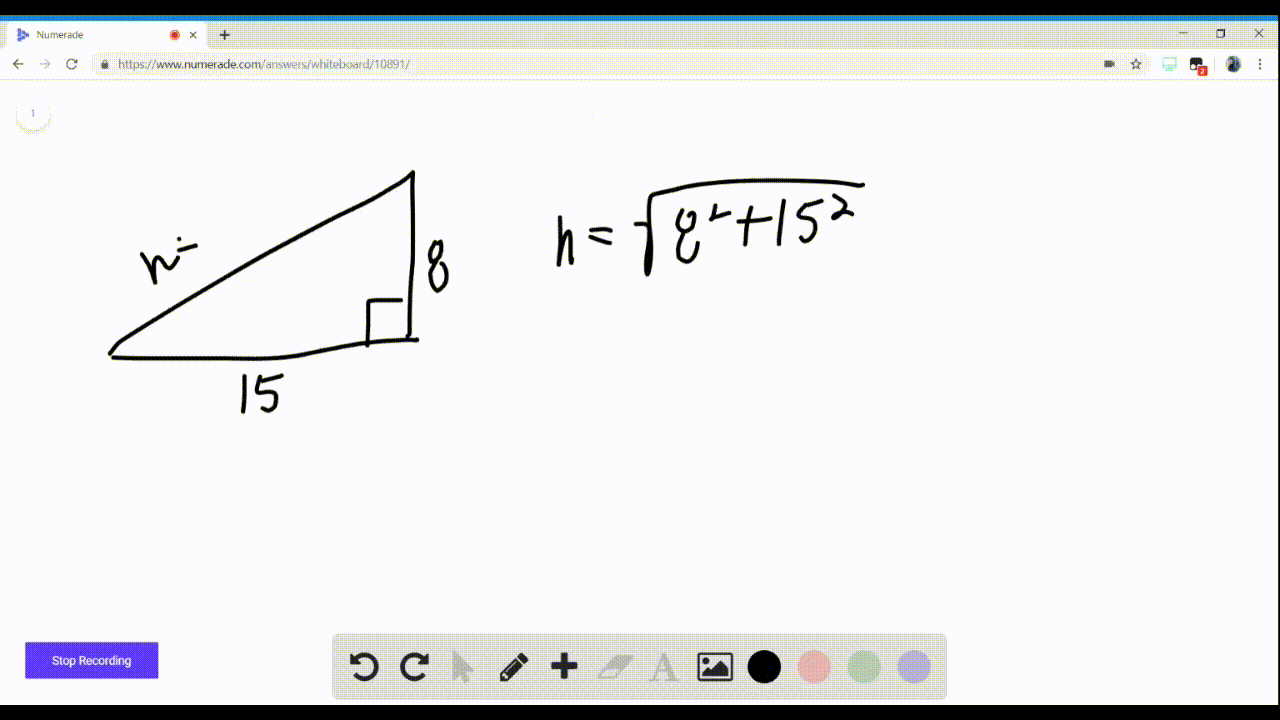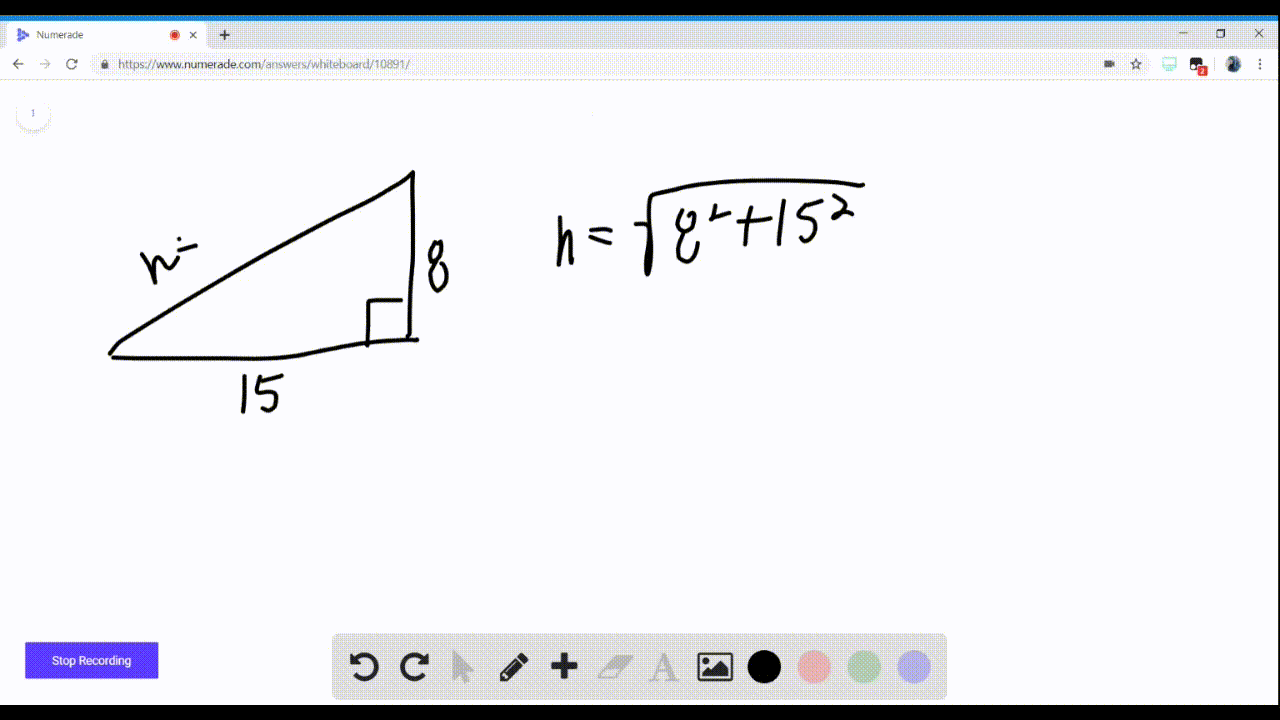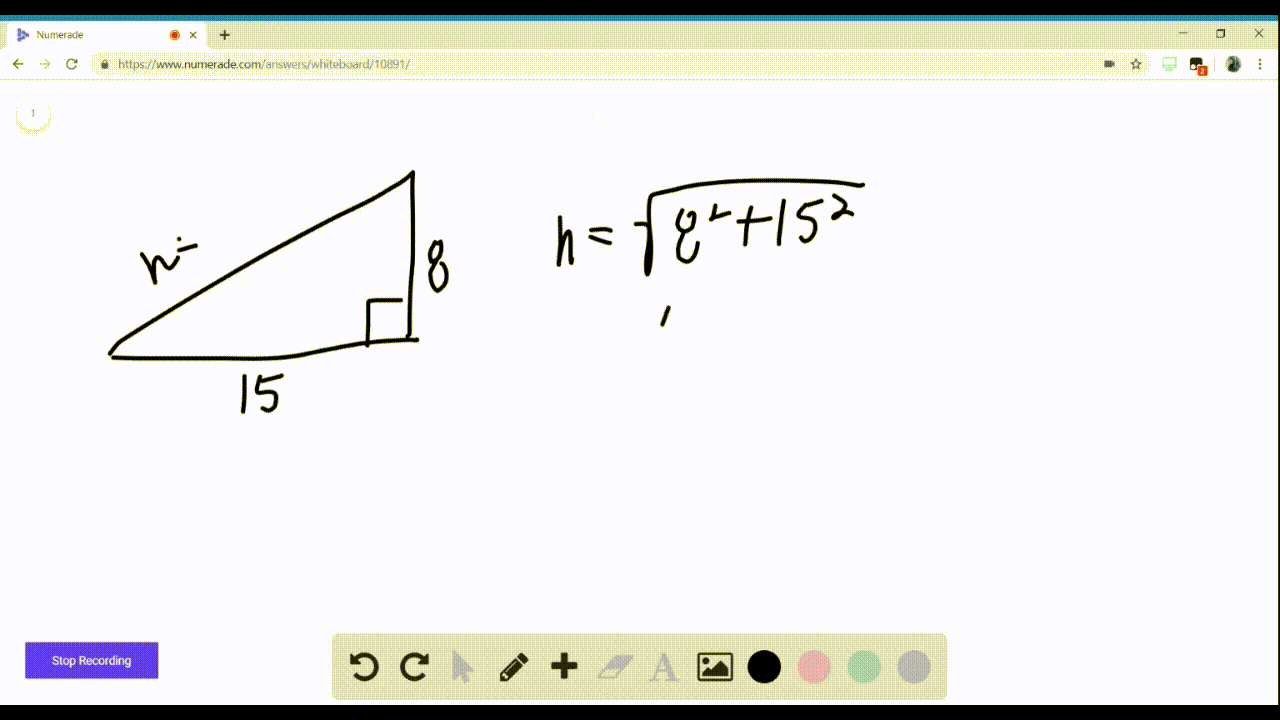



Solved In Exercises 5 8 Use Identities To Find T




Showing That Int 0 Pi Frac Cos N Theta Cos Theta Cos Theta 0 D Theta Pi Frac Sin N Theta 0 Sin Theta 0 Mathematics Stack Exchange
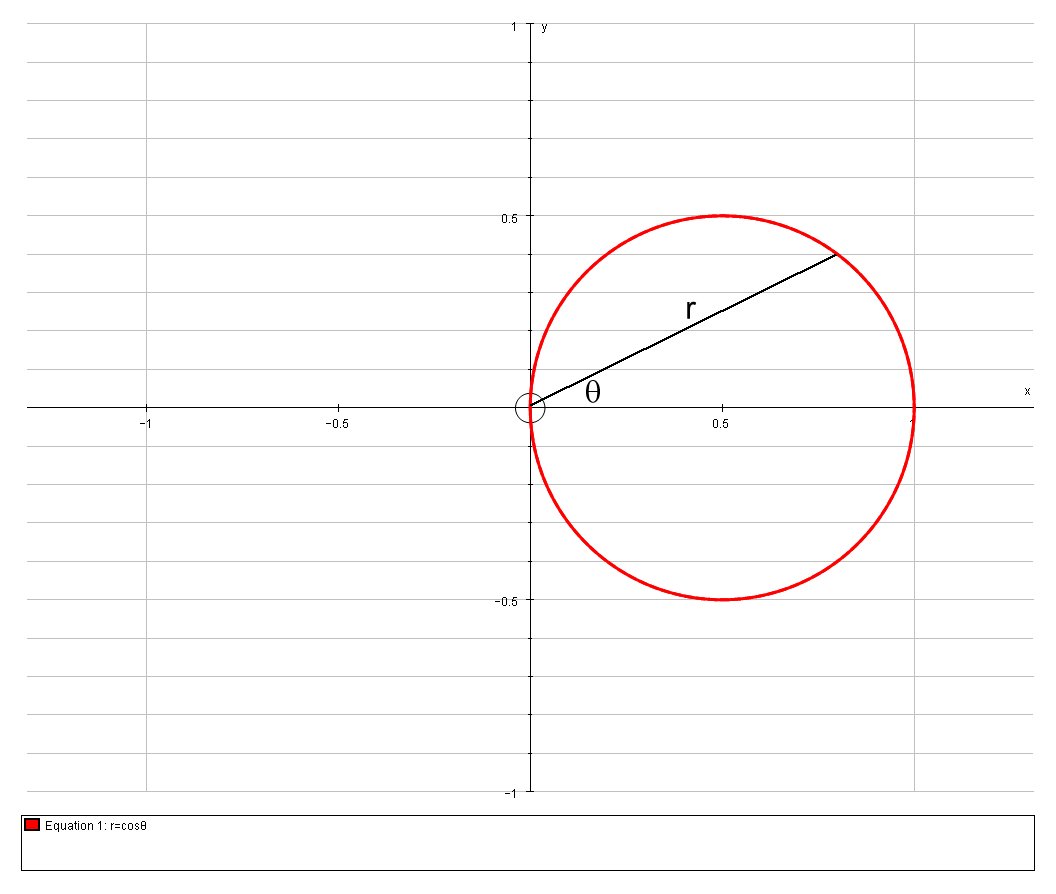



Calculate The Area Bounded By The Polar Curve R Cos Theta Socratic




Math 222 Quiz 6 Take Home Solutions Problem 1 A 1 Point Use




Find The Critical Numbers Of The Function F Theta Chegg Com



Mfg Inverse Trigonometric Functions




Find The Area Enclosed By Circles R 3 Cos Theta And R 3 Sin Theta Mathematics Stack Exchange




If X 2costheta Cos 2theta And Y 2sintheta Sin 2theta Find D 2ydx 2 Theta Pi 2



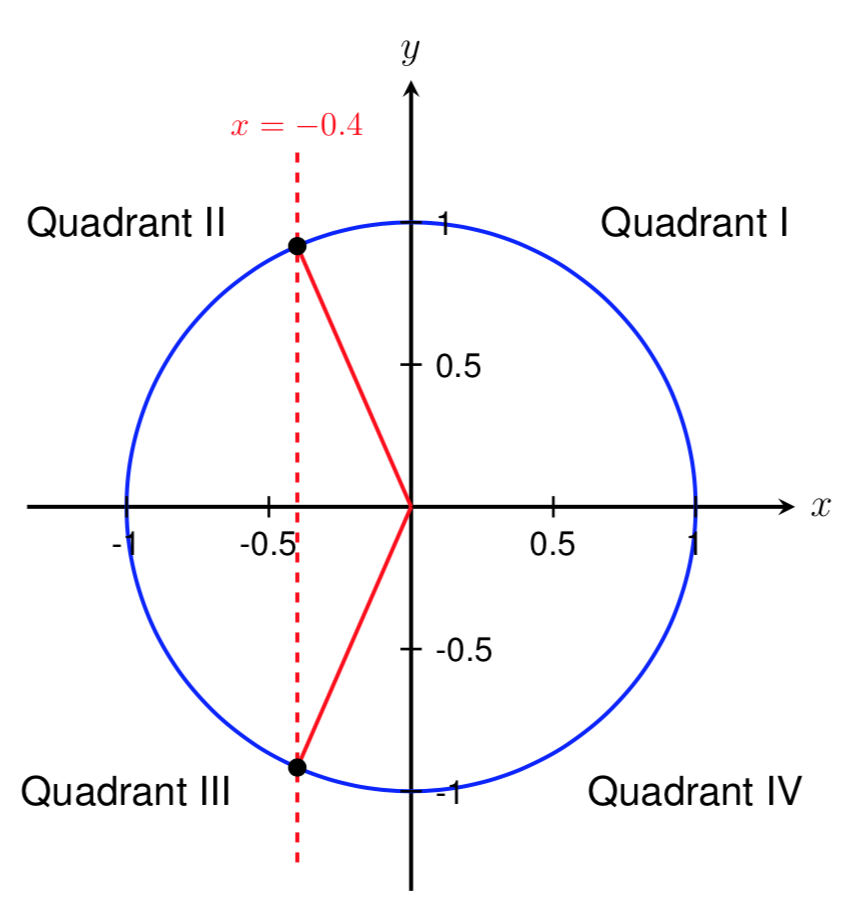
Solve 2 Cos 2 Theta Sin Theta Le 2 Where Pi 2 Le The




If Tan Theta Sectheta Sqrt3 0 Theta Pi Then Theta Is Equal To




If Sin Pi Cos Theta Cos Pi Sin Theta Then Of The Value Cos Theta Pi 4 Is Youtube
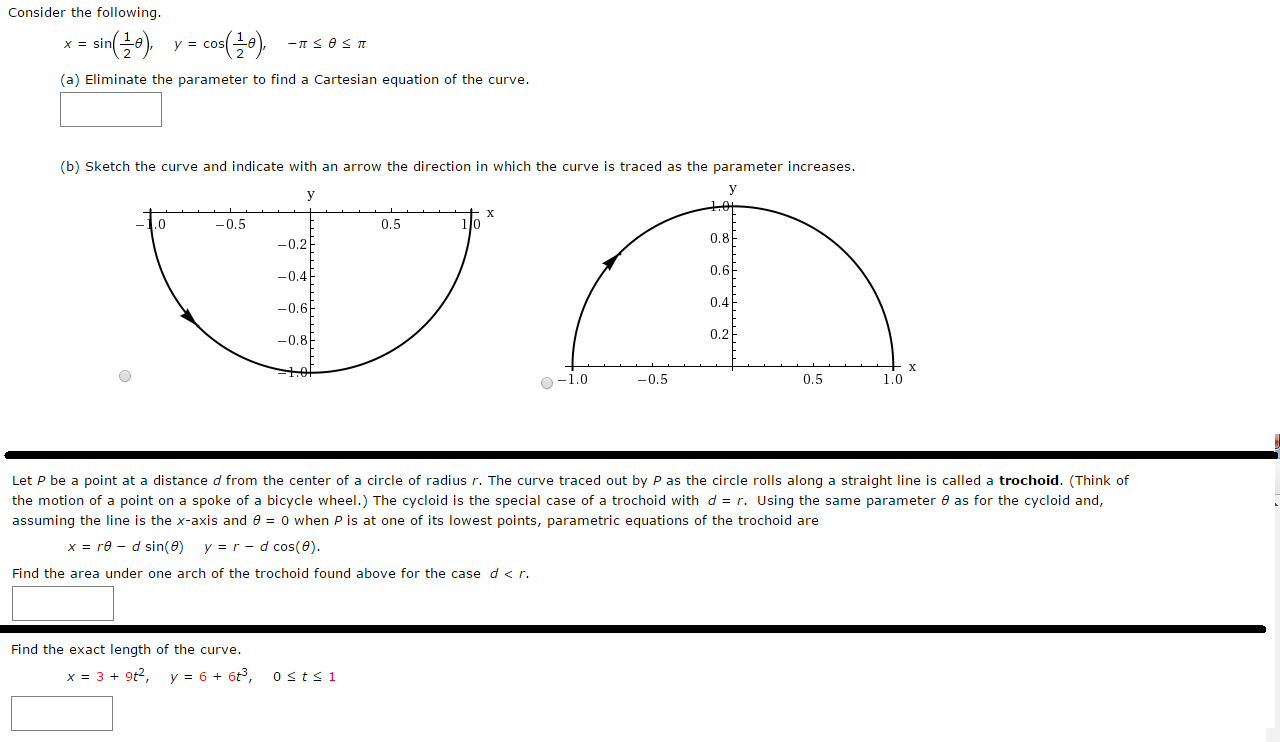



Consider The Following X Sin 1 2 Theta Y Chegg Com




Find The Equation Of The Tangent And The Normal To The Following Curve At The Indicated Point X Theta Sintheta Y 1 Costheta At




Find The Exact Values Of Sin 8 2 Cos 8 2 And Tan 8 2 For The Given Condition 3 Tan 8 3 180 8 90 Wyzant Ask An Expert




Find Cos 8 Frac P 2 If Sin 8 0 57 Gauthmath




This Question Has Statement Which Is True Or False 5 If Pi 9 Theta Pi 2 Then The Value Of Sqrt 1 Sin 2theta Cos Theta Sin Theta



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿