· If it is 0 throughout the entire graph it means f (x) is describing a straight line Just as f'(x)=0 does not tell you what the constant value is for f (x), f"(x)=0 does not tell you what the slope or yintercept of the line is or any other dataHow To Tell Where f (x) is Less Than 0 or Greater Than 0Determine composite and inverse functions for trigonometric, logarithmic, exponential or algebraic functions as part of Bitesize Higher Maths
Solved Consider The Function Defined By F X Y 24 1 2 When X Y 0 0 And F X Y 0 When X Y 0 0 A State The Definition Of Course Hero
What does f(x)=0 mean
What does f(x)=0 mean- · In order to find what value (x) makes f(x) undefined, we must set the denominator equal to 0, and then solve for x f(x)=3/(x2); · This function f (x) =7x−5 means that each time we plug in a value of x we would multiply it by 7 then subtract 5 f (x)=7x−5 → This our function with just x Lets try substituting different values for x f (3)=73−5=21−5=16 → If substitute x by 3, this is what we get




Counting Closed Orbits For The Dyck Shift Topic Of Research Paper In Mathematics Download Scholarly Article Pdf And Read For Free On Cyberleninka Open Science Hub
Critical Points Definition of a critical point a critical point on f (x) occurs at x 0 if and only if either f ' (x 0) is zero or the derivative doesn't exist Extrema (Maxima and Minima) Local (Relative) Extrema Definition of a local maxima A function f (x) has a local maximum at x 0 if and only if there exists some interval I containing x4 Answers4 Hint f can't have a positive maximum at c since then f(c) > 0, f ′ (c) = 0, f ″ (c) ≤ 0 implies that f ″ (c) f ′ (c) − f(c) < 0 Similarly f can't have a negative minimum Hence f = 0 Let x = c be the x coordinate of absolute max of f(x) on a, bA market for the trading of currencies For example, one may buy dollars or sell pounds on a forex market Foreign exchange is one the largest and most liquid markets in the world Trading occurs overthecounter, and most of the major players are governments, banks, and speculators Forex markets are often used in hedging strategies
We set the denominator,which is x2, to 0(x2=0, which is x=2) When we set the denominator of g(x) equal to 0, we get x=0 So x cannot be equal to 2 or 0 Please click on the image for a better understandingA) If f'(x) >0 on an interval, then f is increasing on that interval b) If f'(x) 0 on an interval, then f is concave upward on that interval d) If f''(x)Given f (x) = 3x 2 – x 4, find the simplified form of the following expression, and evaluate at h = 0 This isn't really a functionsoperations question, but something like this often arises in the functionsoperations context
· 'function of x' f(x) basically means y, and f'(x) means dy/dx The x can have a value, so for example, f(x) = 2x 1, then f(1) = 3 that is as good as I can explain it!!!Hi Monica, I have reproduced one of the graphs that you sent us This is the graph of y = f(x) First I want to label the coordinates of some points on theAt x = 0, the derivative of f(x) is therefore 2, so we know that f(x) is an increasing function at x = 0 At x = 1, the derivative of f(x) is df dx (1) = 9 ¢12 ¡12¢12 = 9¡122 = ¡1;




Second Derivative Test Video Khan Academy




Justification With The Mean Value Theorem Table Video Khan Academy
$$ \displaystyle\lim_{h\to 0} \frac{f(xh)f(x)}{(xh) x} Without the limit , this fraction computes the slope of the line connecting two points on the function (see the lefthand graph below) The only thing the limit does is to move the two points closer toClearly, h(x) = (mx b)(nx c) is a polynomial of degree 2 and h(x) has two roots The respective roots are when f(x) = 0 and g(x) = 0 This means the graph of h(x) crosses the xaxis at the same two points as f(x) and g(x) Thus, if there are points of tangency then they must occur at these common points on the xaxisBy $f(x) = x^2 4$ I am telling you that if you input a number $x$ to this function then the function squares $x,$ subtracts 4 and returns the result Thus for example if $x = 3$ then $y = f(3) = 3^2 4 = 9 4 = 5$ To graph this function I would start by choosing some values of $x$ and since I get to choose I would select values that make the arithmetic easy
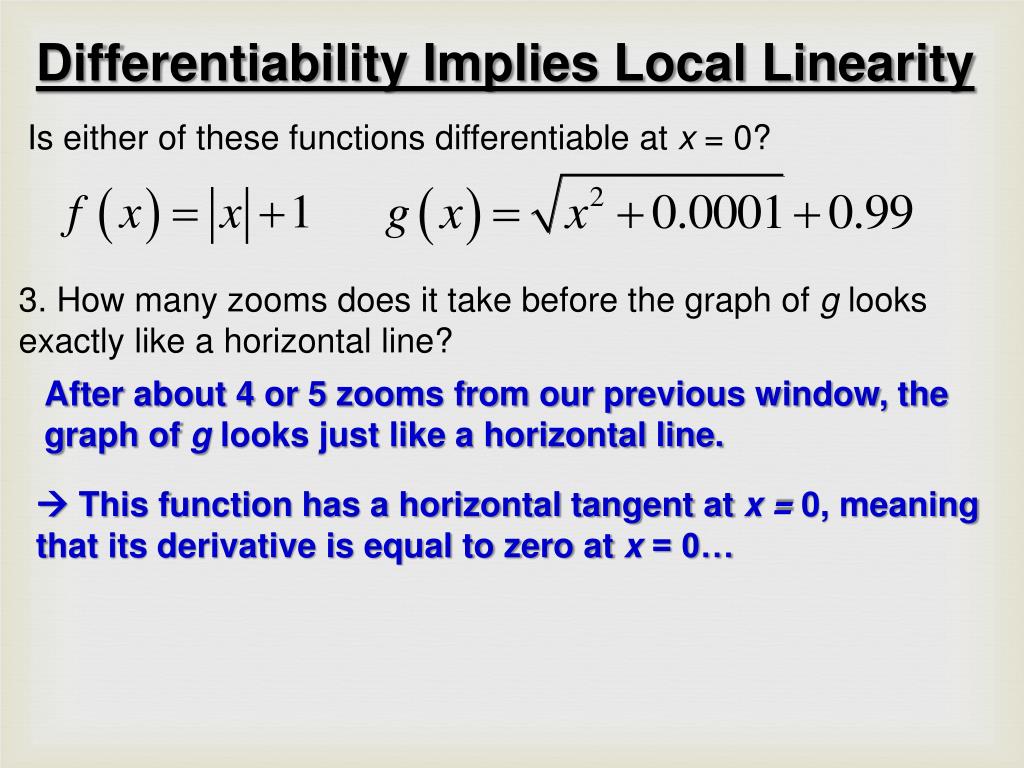



Ppt Differentiability Local Linearity Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
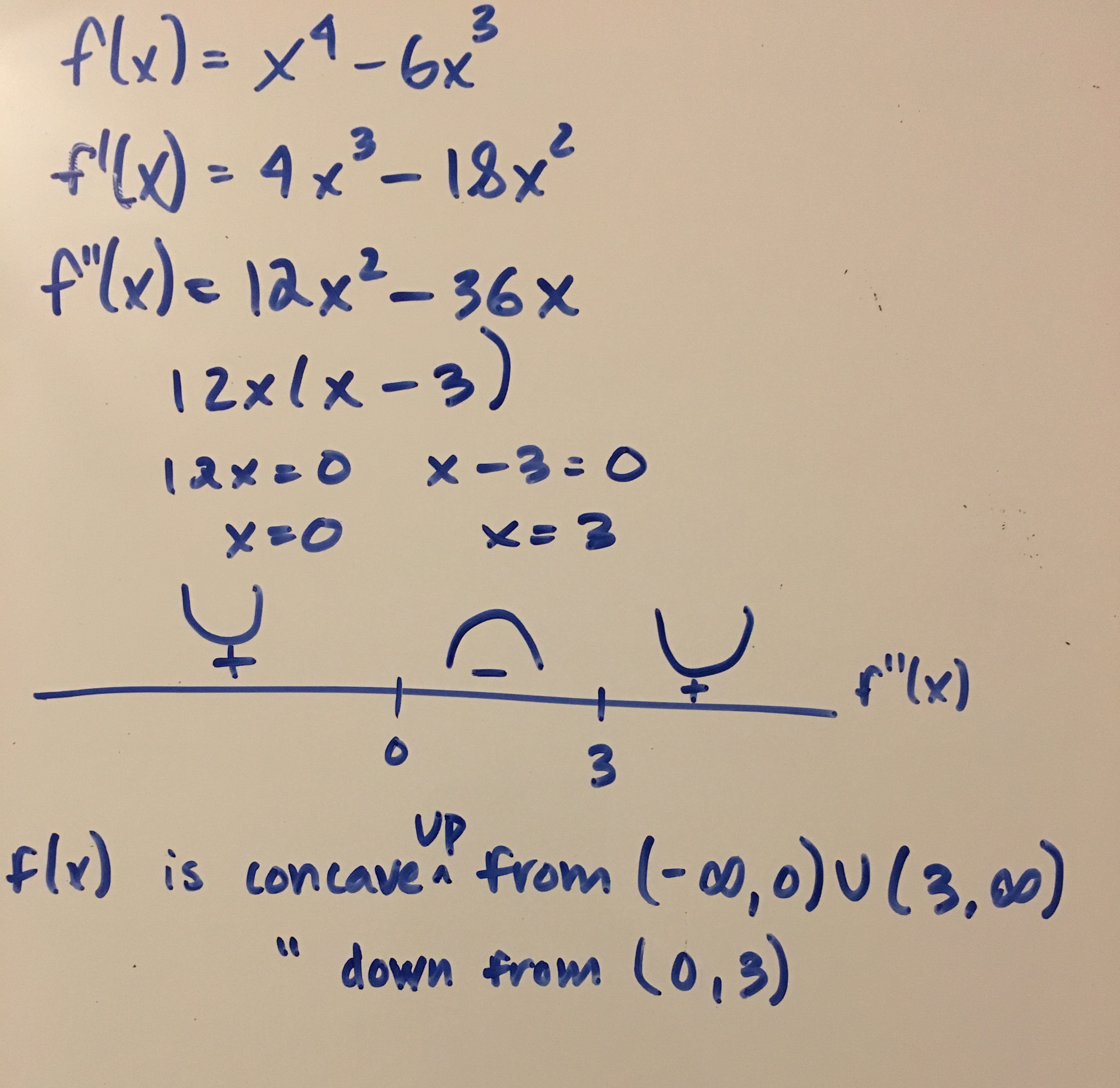



How Do You Ise Interval Notation Indicate Where F X Is Concave Up And Concave Down For F X X 4 6x 3 Socratic
If, instead, you define f as f (x) = { 1 N 1 − e 2 π i x 1 − e 2 π i x / N x ≠ 0 1 N 1 − 1 x = 0 Then the resulting function is defined at 0 and, because the limit as x → 0 is 1 = f (0), f is continuous at 0, which is quite a nice property for it to have · The term you need to search for is slice x startendstep is the full form, Here we can omit to use a default value start defaults to 0 , end defaults to the length of the list, and step defaults to 1 And hence x means same as x 0len (x)1 Share Improve this answer answered May 1 ' at 630 Adiraamruta · X the inputs, factors or whatever is necessary to get the outcome (there can be more than one possible x) F the function or process that will take the inputs and make them into the desired outcome Simply put, the Y=f(x) equation calculates the dependent output of a process given different inputs



Differentiability And Continuity Video Khan Academy




13 Probabilistic Contagion And Models Of Influence Machine Learning With Graphs Weights Biases
Yeah, f (x) is the normal function, f' (x) is the first differential and f'' (x) is the second differential, ad infinitum Hey I'm a little late to this post, but I just looked about the meaning of f' (x) and found your post very helpful, thanks But I'd just like to clarify about what you meant by 'ad infinitum'Solve your math problems using our free math solver with stepbystep solutions Our math solver supports basic math, prealgebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and more12 · We let Δz = f(41, 08) − f(4, π / 4) The total differential dz is approximately equal to Δz, so f(41, 08) − f(4, π / 4) ≈ dz ⇒ f(41, 08) ≈ dz f(4, π / 4) To find dz, we need fx and fy fx(x, y) = siny 2√x ⇒ fx(4, π / 4) = sinπ / 4 2√4 = √2 / 2 4 = √2 / 8 fy(x



Relations Graphs And Functions




If F X Satisfies The Requirements Of Lagrange S Mean Value Theorem On 0 2 And If F 0 0 An Youtube
Proof of the Sum Law If lim x → cf(x) = L and lim x → cg(x) = M, then lim x → cf(x) g(x) = L M Suppose ϵ > 0 has been provided This is the first line of any deltaepsilon proof, since the definition of the limit requires that the argument work for any epsilon Define ϵ2 = ϵ 2 We are defining a new, smaller epsilon · f (x,y) is function in x and y If you draw this in R 3, the function will lie in the xyplane The domain of the function is the xy plane or some subset of it The graph of the function is the ordered triples (x, y, z) for which z = f (x, y) Example z = ln (xy) The domain is the portion of the plane for which xy > 0, which is the interiorSince we're looking for f (x)=0, we're looking for y=0 since y and f (x) can be interchanged In other words, we are looking for the xintercept, since y=0 for all xintercepts So we substitute 0 in for f (x) and we get Now we solve for x




Counting Closed Orbits For The Dyck Shift Topic Of Research Paper In Mathematics Download Scholarly Article Pdf And Read For Free On Cyberleninka Open Science Hub




The Derivative
When the first derivative is 0 at a given point, it means the tangent line is horizontal on a graph, or that the function is static at that point If it is true for the entire function it means that f (x) is a constant—that x does not affect the value in any waySo f(x) is a decreasing function at x = 1 The Meaning of the Second Derivative The second derivative of a function is the derivative of the derivative of that functionIf F(x)=x has no real solution then also F(F(x)=x has no real solution
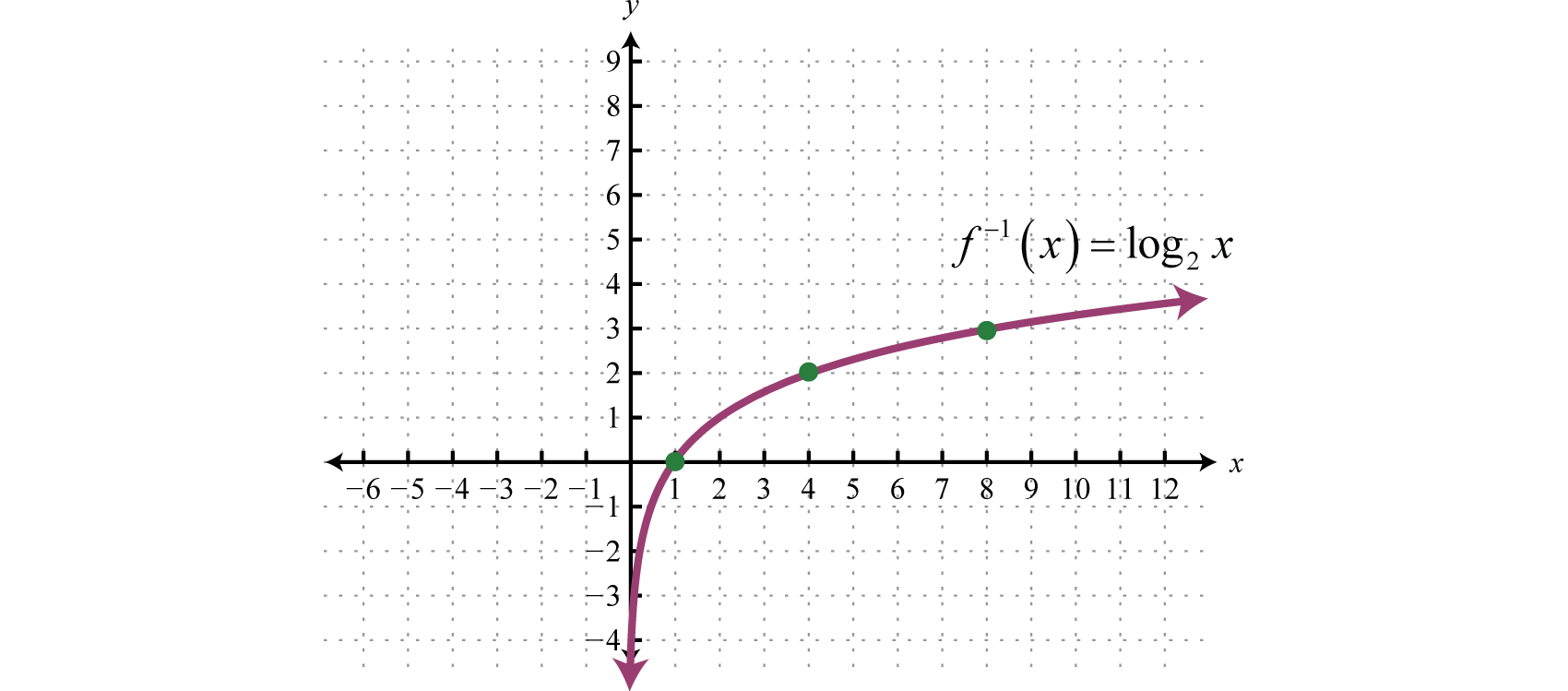



Logarithmic Functions And Their Graphs




Find C Of Lagrange S Mean Value Theorem F X X X 1 X 2 Where X 0 1 2 Brainly In
F(x) means that we have a function of x The zero of the function f(x)=2x2 is the xvalue that makes f(x) = 0 So we can just set the function equal to 0, and then solve for x! · Videos you watch may be added to the TV's watch history and influence TV recommendations To avoid this, cancel and sign in to on your computer An error occurred while retrieving sharingDon't embarrass yourself by pronouncing (or thinking of) " f ( x ) " as being " f times x ", and never try to "multiply" the function name with its parenthesised input




F X Y 0 Meaning Subscribe To Rss



Calculus Limit Function Take The Limit As X Approaches
Definition of Y = f (X) In this equation X represents the input of the process and Y the output of the procees and f the function of the variable X Y is the dependent output variable of a process It is used to monitor a process to see if it is out of control, orThe Function which squares a number and adds on a 3, can be written as f (x) = x2 5 The same notion may also be used to show how a function affects particular values Example f (4) = 4 2 5 =21, f (10) = (10) 2 5 = 105 or alternatively f x → x2 5 The phrase "y is a function of x" means that the value of y depends upon the value of\Fourier sine series" Computing coe cients in an orthogonal expansion is just a matter of taking inner products B n =




Solved Explain The Meaning Of Each Of The Following A Chegg Com
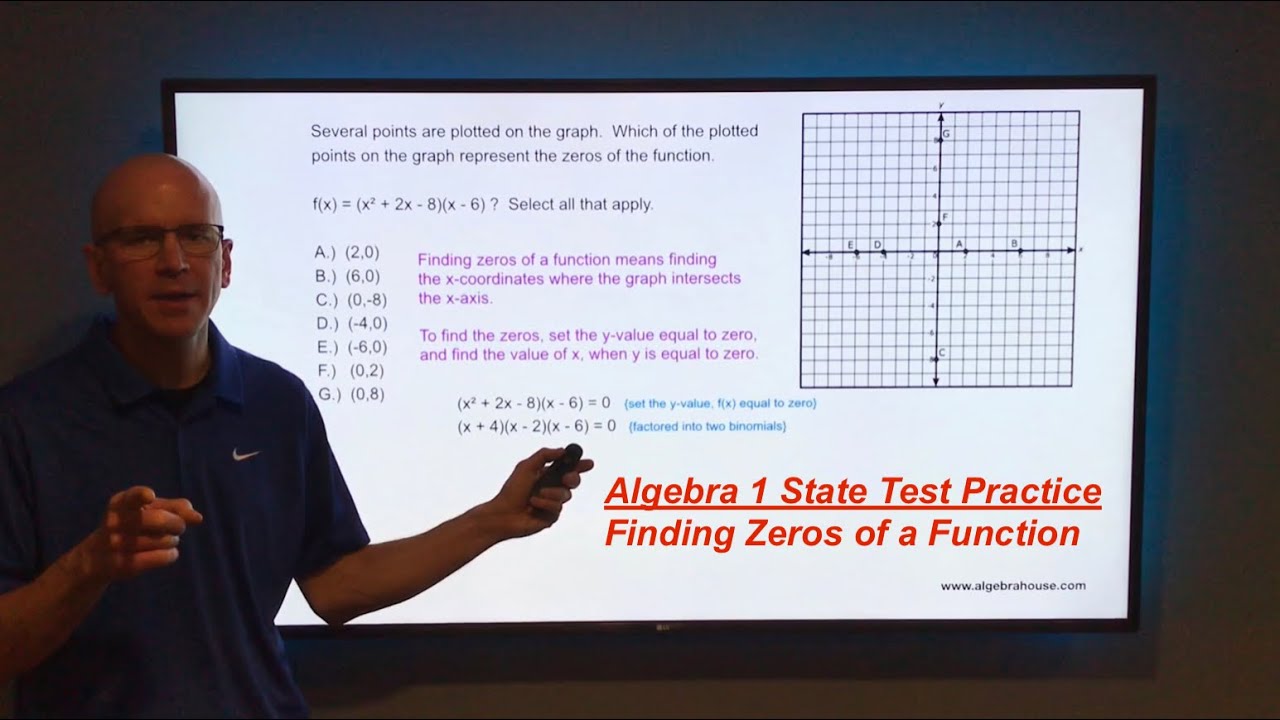



Finding Zeros Of A Function Algebra House
What goes intothe function is put inside parentheses () after the name of the function So f(x)shows us the function is called "f", and "x" goes in And we usually see what a function does with the input f(x) = x2shows us that function "f" takes "x" and squares it Example with f(x) = x2 an input of 4The expression "f (x)" means "a formula, named f, has x as its input variable" It does not mean "multiply f and x "!Could you explain to me how one should go about graphing functions such as f(x), f(x2), and so on Also, how should you explain things such as constants and relationships among functions?
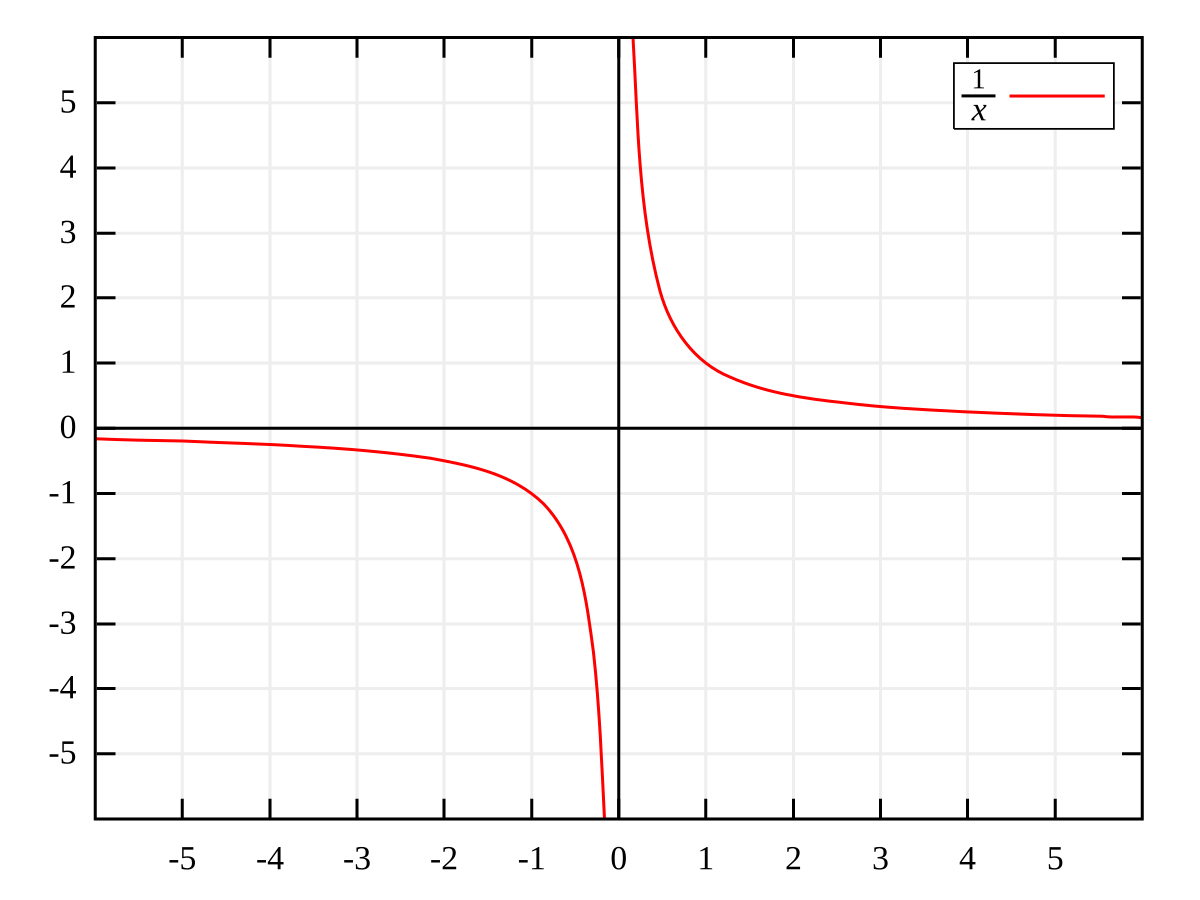



Division By Zero Wikipedia
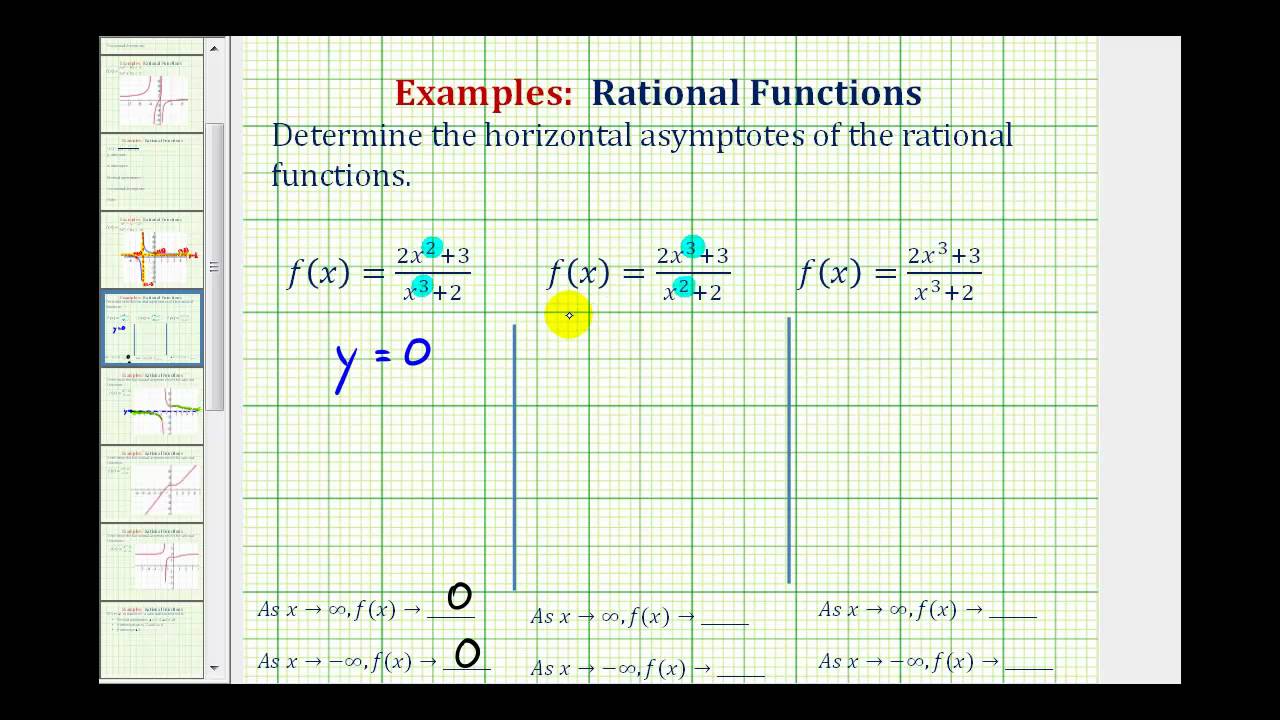



Horizontal Asymptotes And Intercepts College Algebra
· f' (x) The first derivative of a function See calculus If f (x) is equal to x^2 2x 5 then f' (x) is equal to 2x2 by ManMan36 May 23, 16 Flag Get the f' (xThe meaning of infinityThe definition of 'becomes infinite' Let us see what happens to the values of y as x approaches 0 from the right As the sequence of values of x become very small numbers, then the sequence of values of y, the reciprocals, become very large numbersThe values of y will become and remain greater, for example, than 10 y becomes infiniteUsually in basic math it means (f(x)) 2 But sometimes in a class like dynamical systems it will mean f(f(x)) In fact, I prefer the 2nd definition and to insist on writing (f(x)) 2 for the other term But mathematicians are extremely lazy and prefer to write things like sinx instead of sin(x), so I think I'm in the minority on this




Rd Sharma Solutions For Class 12 Maths Chapter 15 Mean Value Theorems Avail Free Pdf
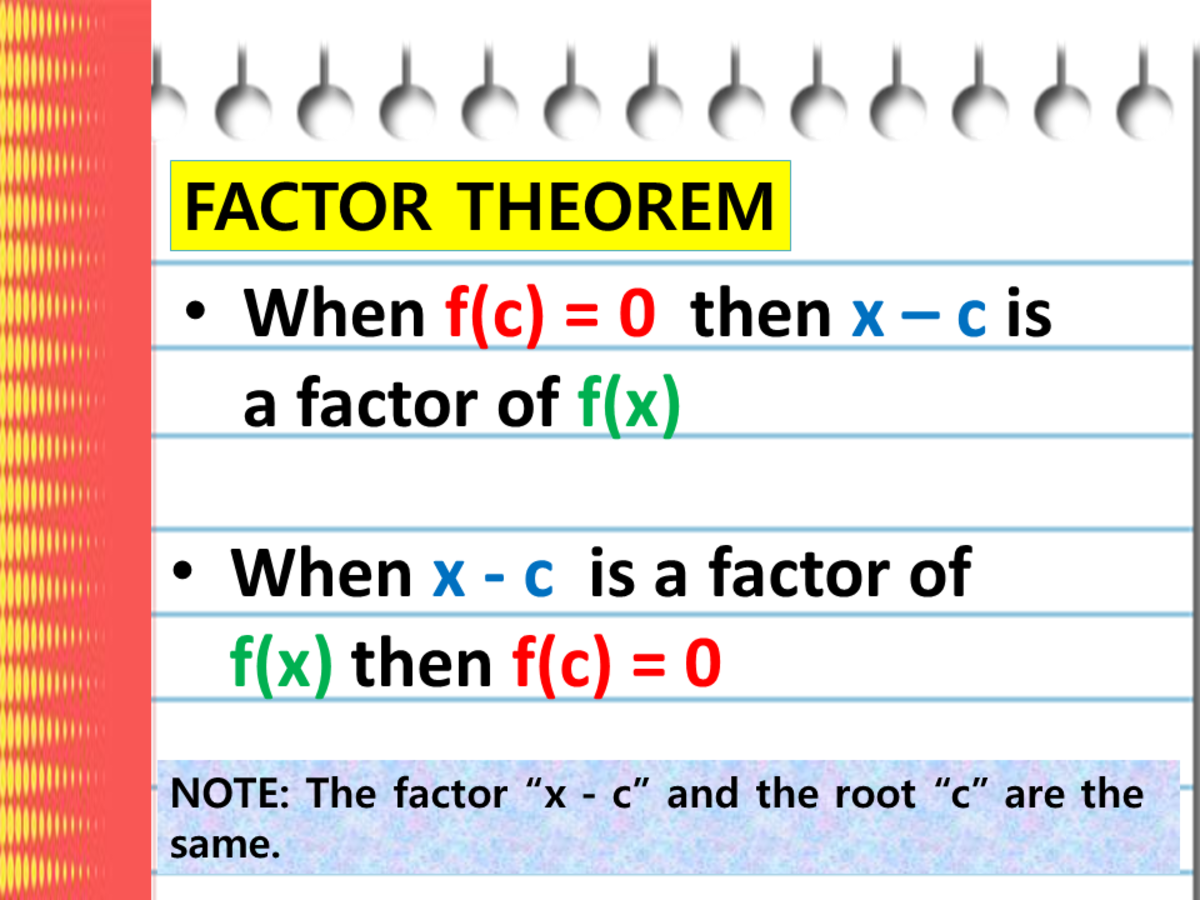



Using The Factor Theorem In Finding The Factors Of Polynomials With Examples Owlcation
Math 113 Homework 1 Solutions Solutions by Guanyang Wang, with edits by Tom Church Exercise 1 Show that 1 p 3i 2 is a cube root of 1 (meaning that its cube equals 1) Proof We can use the de nition of complex multiplication, we have · Note that y = f(x) When f(x) = 0 the graph is on the x axis This is the point ( 18, 0 ) , that is y = 0 and x = 18 Stepbystep explanation New questions in Mathematics Please explain No Links or I will Report Please help me I am trying to get this so0 f(x)sin(nx dx R ˇ 0 sin 2( )dx = 2 Big payo completeness of eigenfunctions means that any smooth function with f(0) = 0 = f(ˇ) can be written f(x) = X1 n=1 B n sin(nx);




Find C Of Lagrange S Mean Value Theorem F X X X 1 X 2 Where X 0 1 2 Brainly In
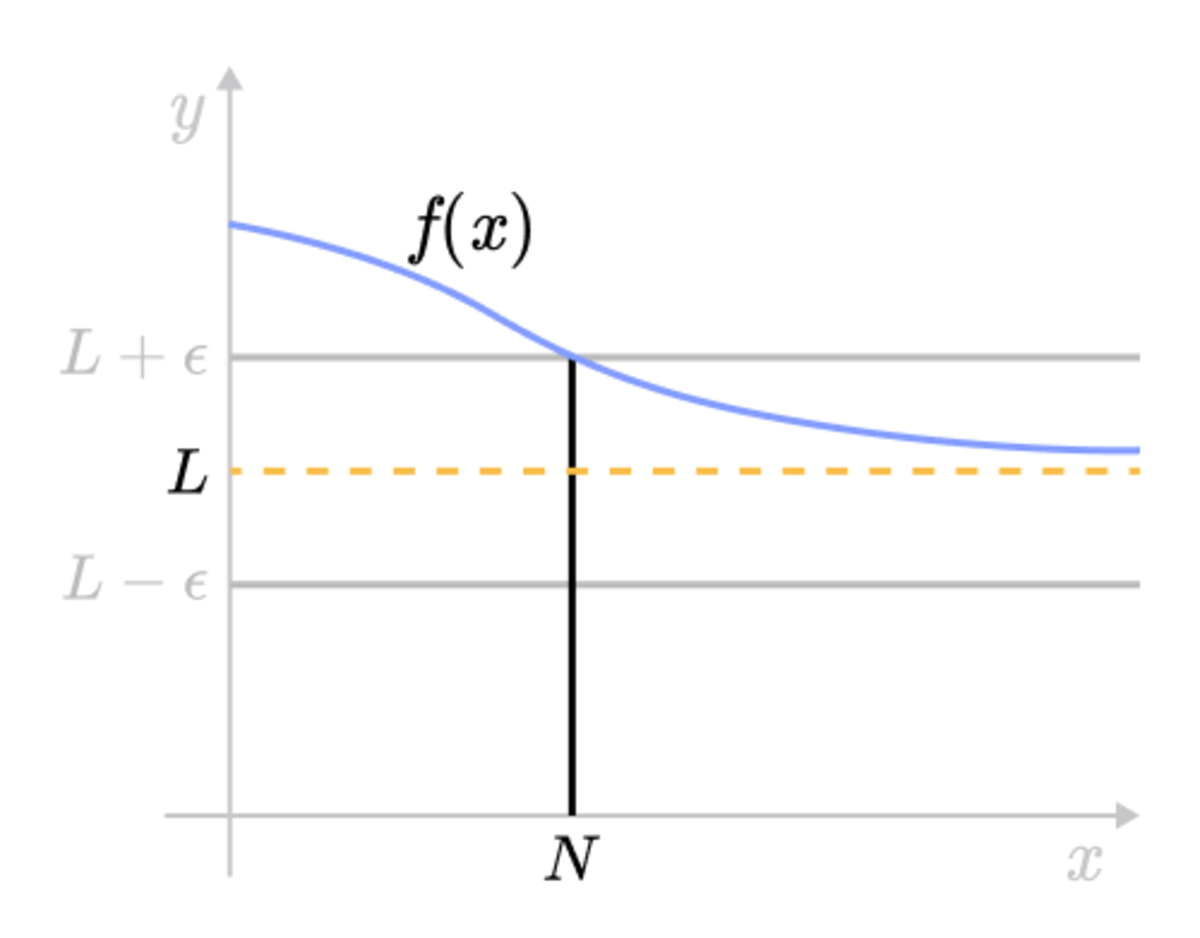



Epsilon Delta Definition Of A Limit Brilliant Math Science Wiki
The f is because there's no need for the operation to be done in double I expect there's more chance of an implementation where 10/i would be significantly slower for no benefit (software float emulation, indifferent optimization), than one where 10f is significantly slower for no benefit (if double is faster than float that's because you have fp hardware, so conversion between the two · The Ftest of overall significance indicates whether your linear regression model provides a better fit to the data than a model that contains no independent variablesIn this post, I look at how the Ftest of overall significance fits in with other regression statistics, such as RsquaredRsquared tells you how well your model fits the data, and the Ftest is related to it · The derivative, f'(x), can be interpreted as "the slope of the tangent line" f'(x)> 0 means all tangent lines have positive slope are going up to the right Also "if x> 0, then f'(x)< 90" so for x positive, the derivative is negative which means tangent lines are going down to the right



Solved Consider The Function Defined By F X Y 24 1 2 When X Y 0 0 And F X Y 0 When X Y 0 0 A State The Definition Of Course Hero
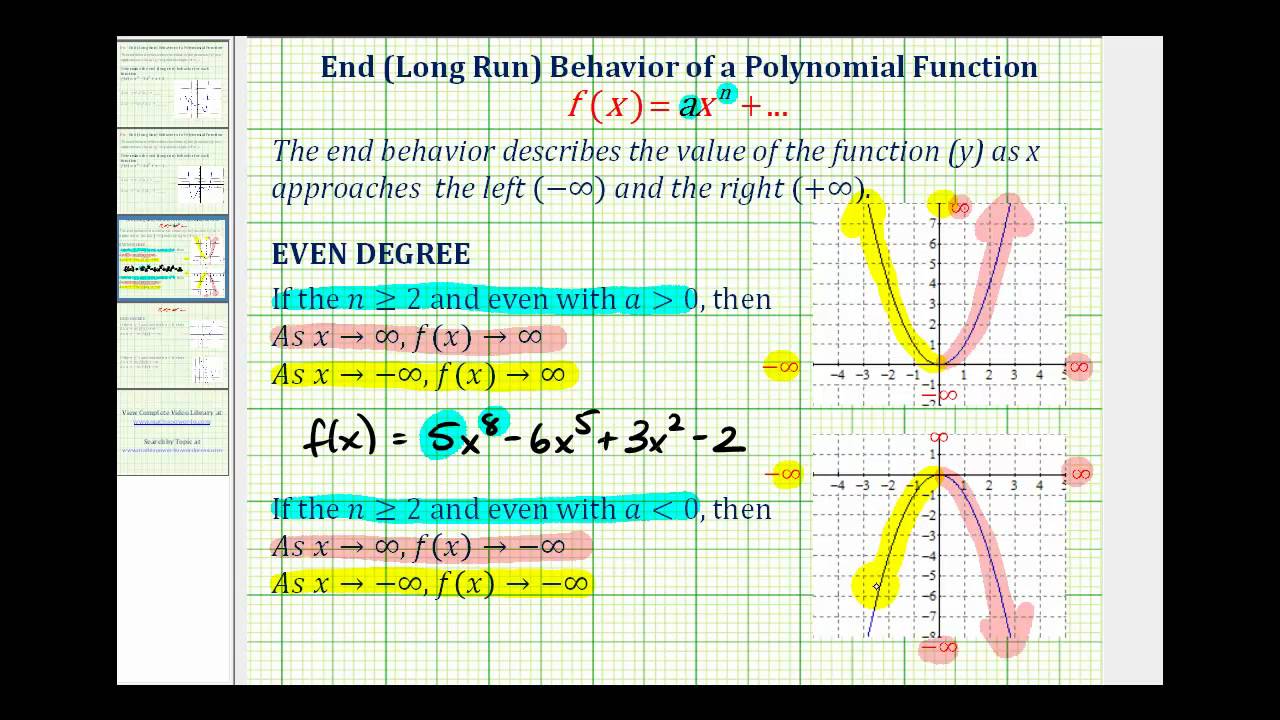



Characteristics Of Power And Polynomial Functions College Algebra
Originally Answered What is the meaning of f' (x) =0 and f' (x) =0?Since Δx not x is the variable that approaches 0, x remains constant, and that limit will be a function of x Since it will be derived from f(x), we call it the derived function or the derivative of f(x) To remind us that it was derived from f(x), we denote it by f '(x) "fprime of xIf f(x) is a function that is defined on an open interval around x=c, and L is a real number, then lim x →c f(x) = L means that For any number ε>0 that we choose, it is possible to find another number δ>0 so that for all x's between cδ and cδ (except possibly at c exactly), f(x
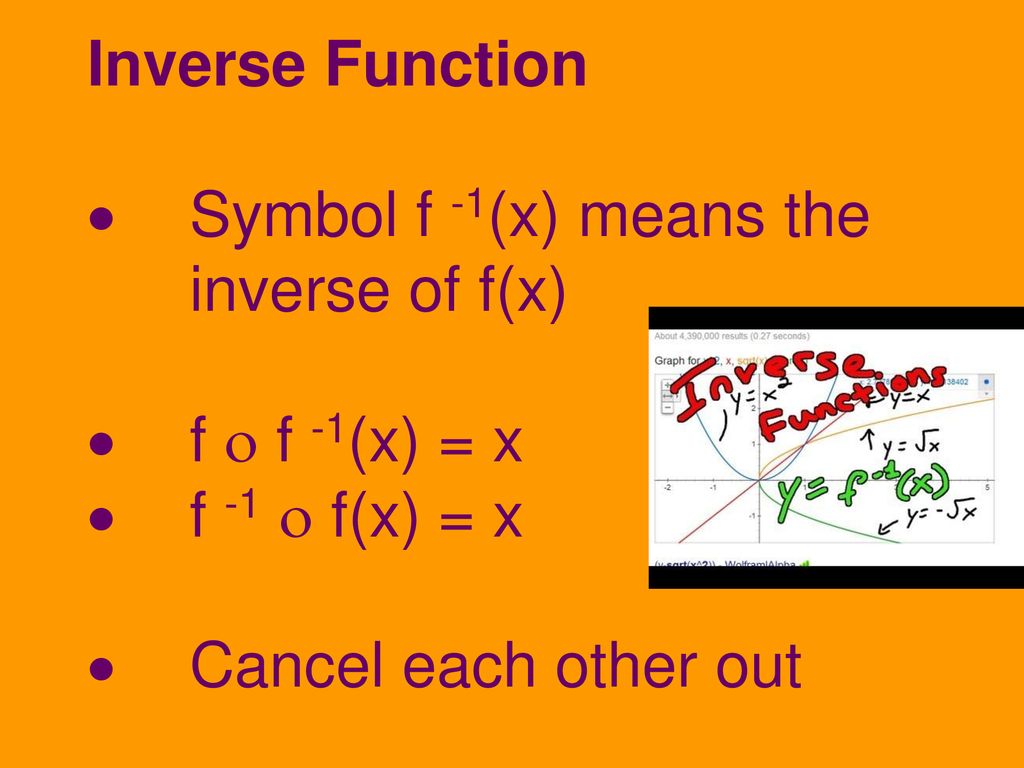



Inverse Function Symbol F 1 X Means The Inverse Of F X Ppt Download




Solved Xy X2 If X Y 0 0 Consider The Function F X Chegg Com




To 64 Consider The Function Y F X X2 6x 5 Q 32 The Math




Answered For The Function F X 4x 16x 25 Bartleby
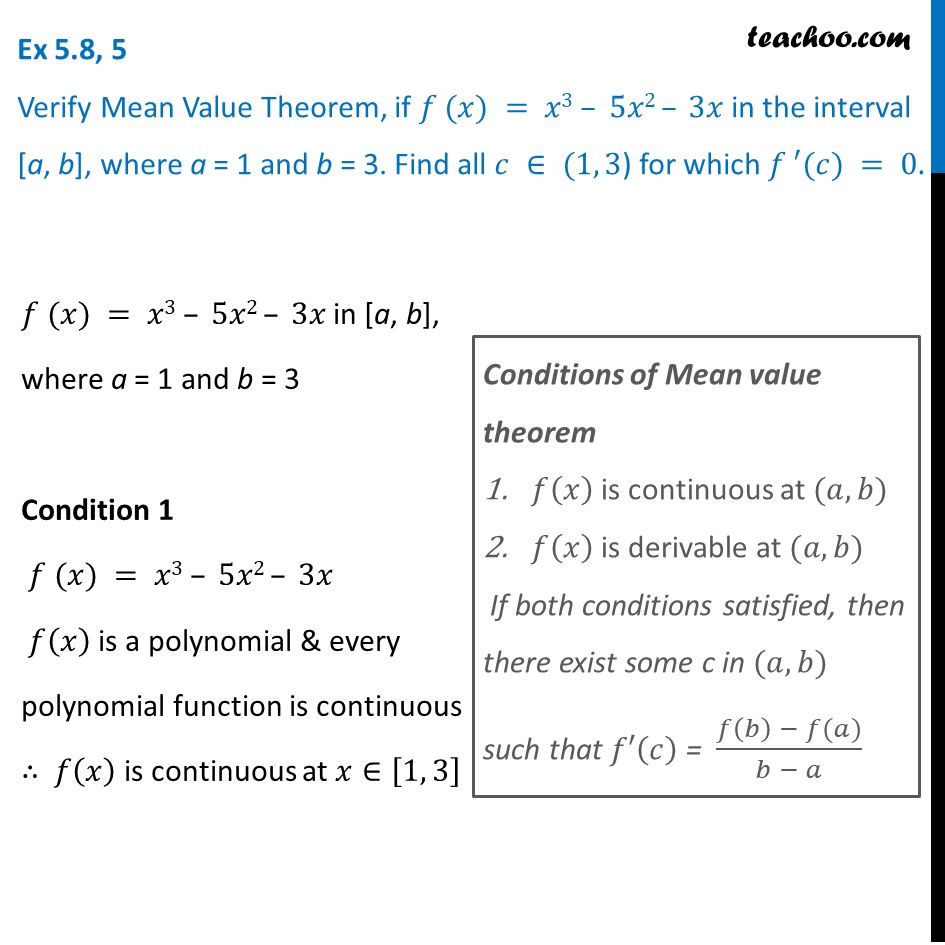



Ex 5 8 5 Verify Mean Value Theorem F X X3 5x2 3x




What Does F N X Mean




Answered Simplify The Following Asymptotic Bartleby




3 3 Rules For Differentiation Ppt Download



What Is The Range Of A Function Expii




The Function F X Is Defined On The Interval 0 1 Find The Domain Of Definition Of The Youtube




Rolle S Theorem Definition Equation Facts Britannica
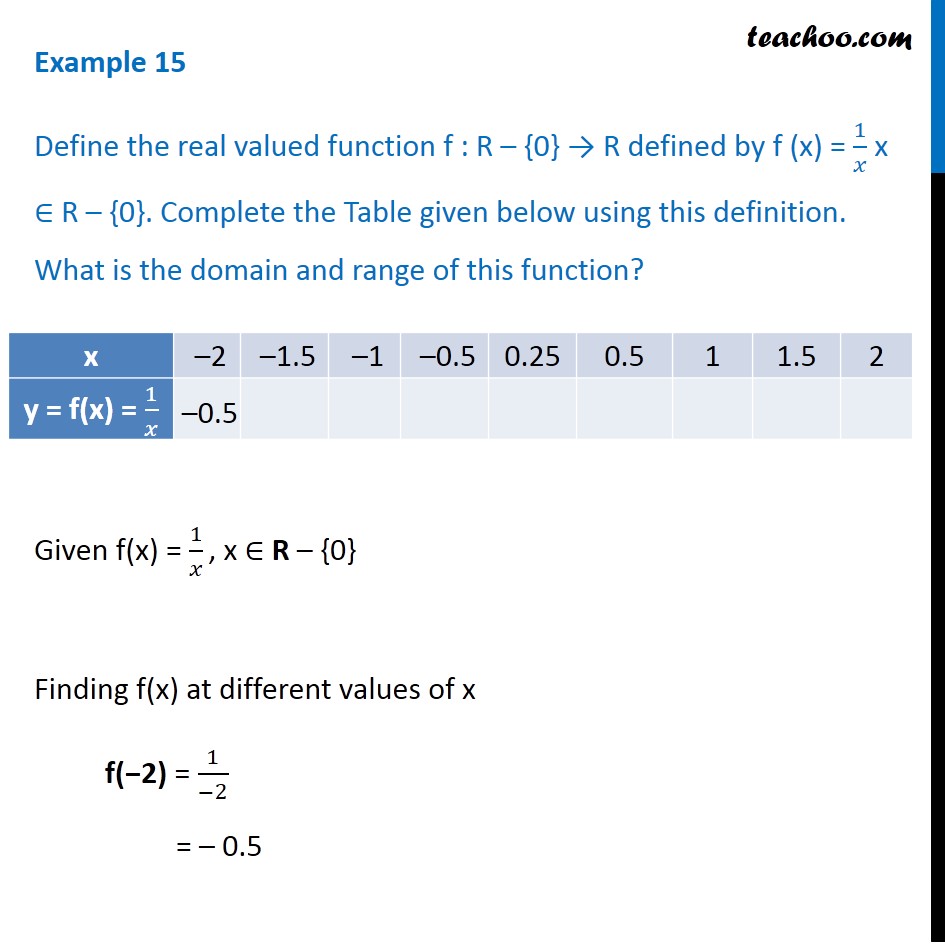



Example 15 F X 1 X What Is The Domain And Range Examples




Prove That F X Sqrt X Is Uniformly Continuous On 0 Infty Mathematics Stack Exchange




4 1 Extreme Values Of Functions Mathematics Libretexts




Consider The Function Defined By The Following O Chegg Com
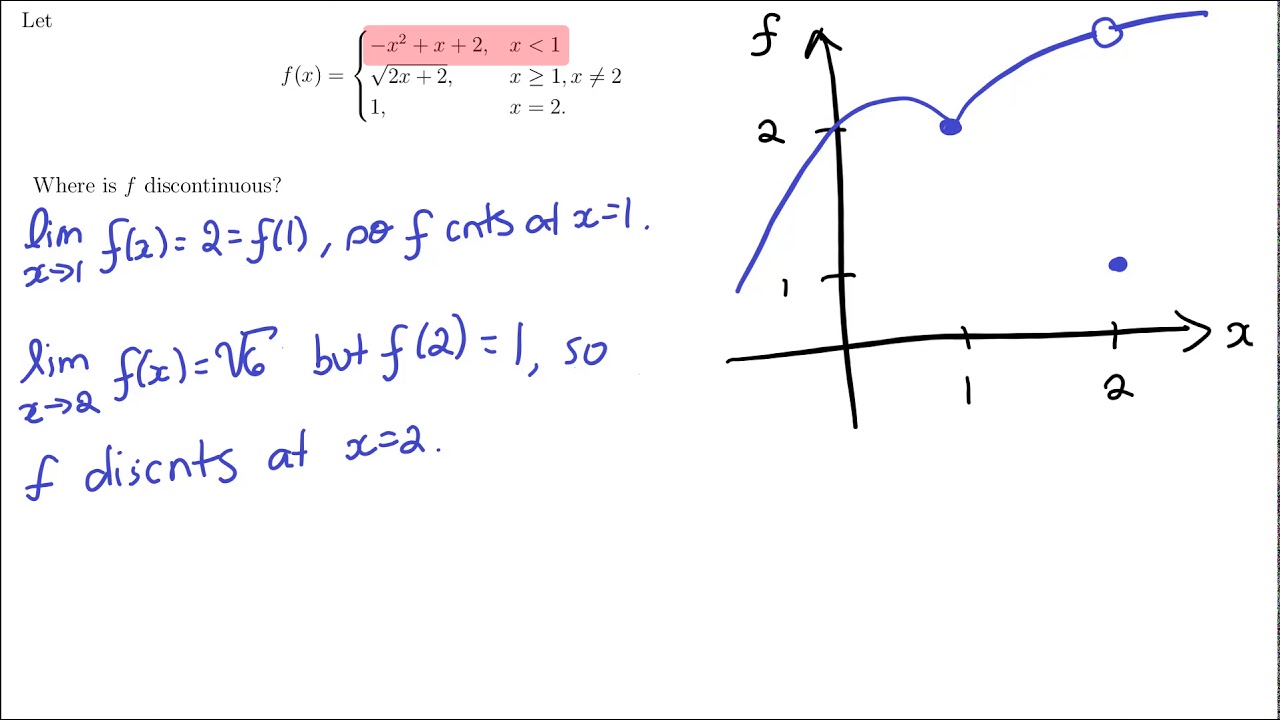



Continuity And Ivt
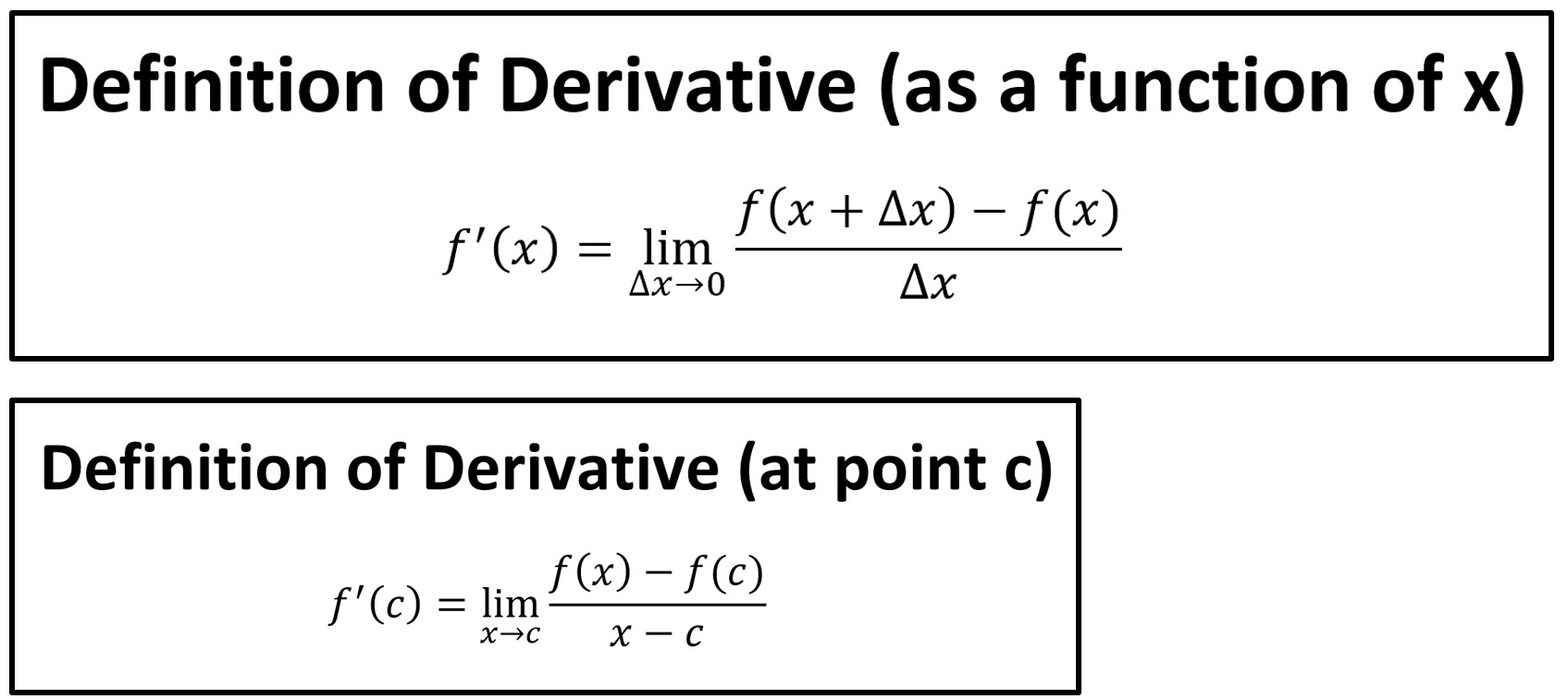



Definition Of Derivative Andymath Com
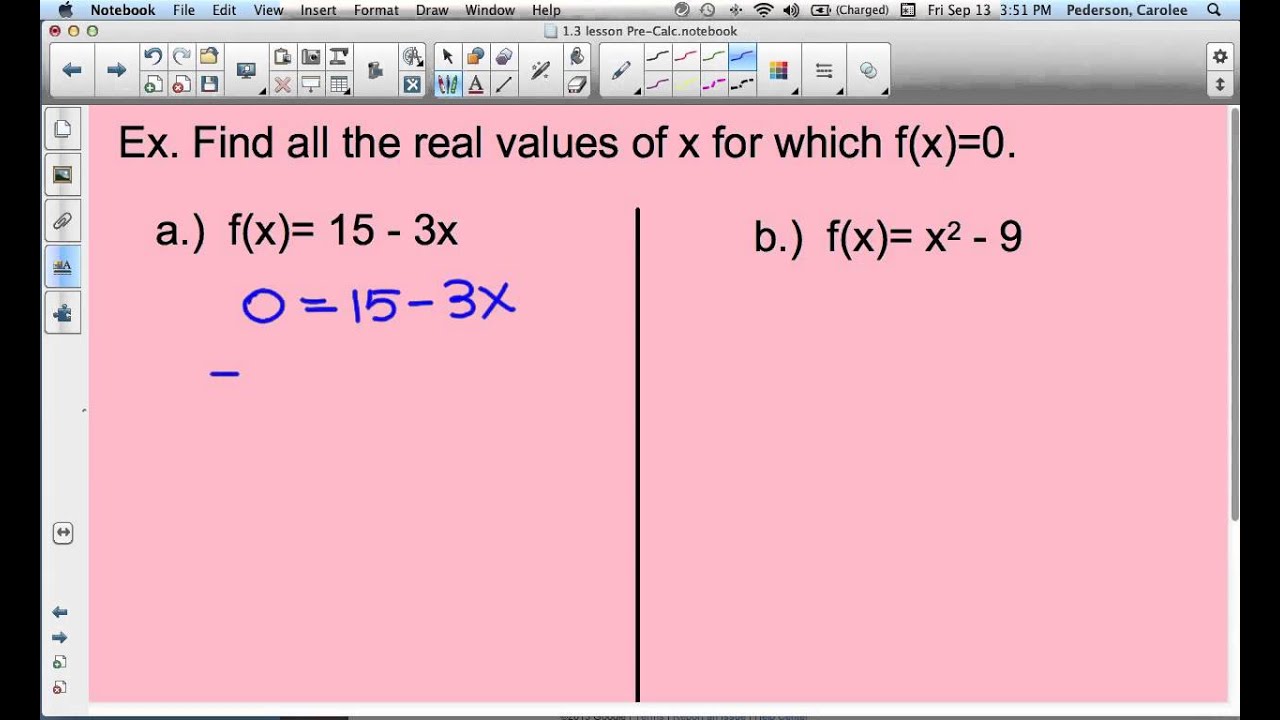



Find Real Values For Fx 0 Youtube




Solved It X 1 Consider The Function F X Y Ja2 0 Chegg Com




Definition 2 Limits




Existence Of Partial Derivatives Not Implies Differentiable Calculus




Quiz 12 True False Math 1525 Calc With Matrices Docsity




The Function F X Is Defined In 0 1 Find The Domain Of F




Need Help On A Question On Monotonicity Mathematics Stack Exchange
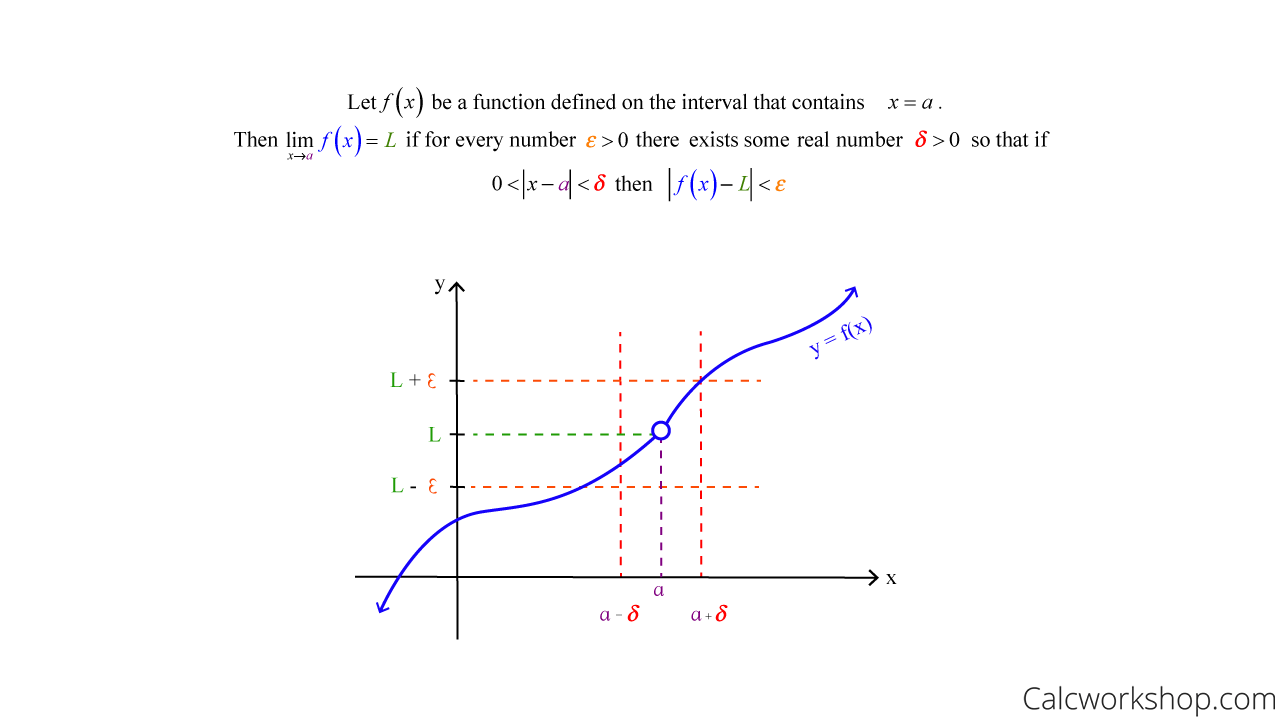



Epsilon Delta Definition Of A Limit Fully Explained




Zero Of A Function Wikipedia



Solved Find The Maclurin Series For F X Sin2x Using The Definition Of A Maclaurin Series Please Show All Detailed Steps Course Hero




On Degree Of Approximation Of The Gauss Weierstrass Means For Smooth Lp Rn Functions Topic Of Research Paper In Mathematics Download Scholarly Article Pdf And Read For Free On Cyberleninka Open Science Hub




Is The Function F X Cos X Even Odd Or Neither Socratic




Let F X Be Defined In 0 1 Then The Domain Of Definition
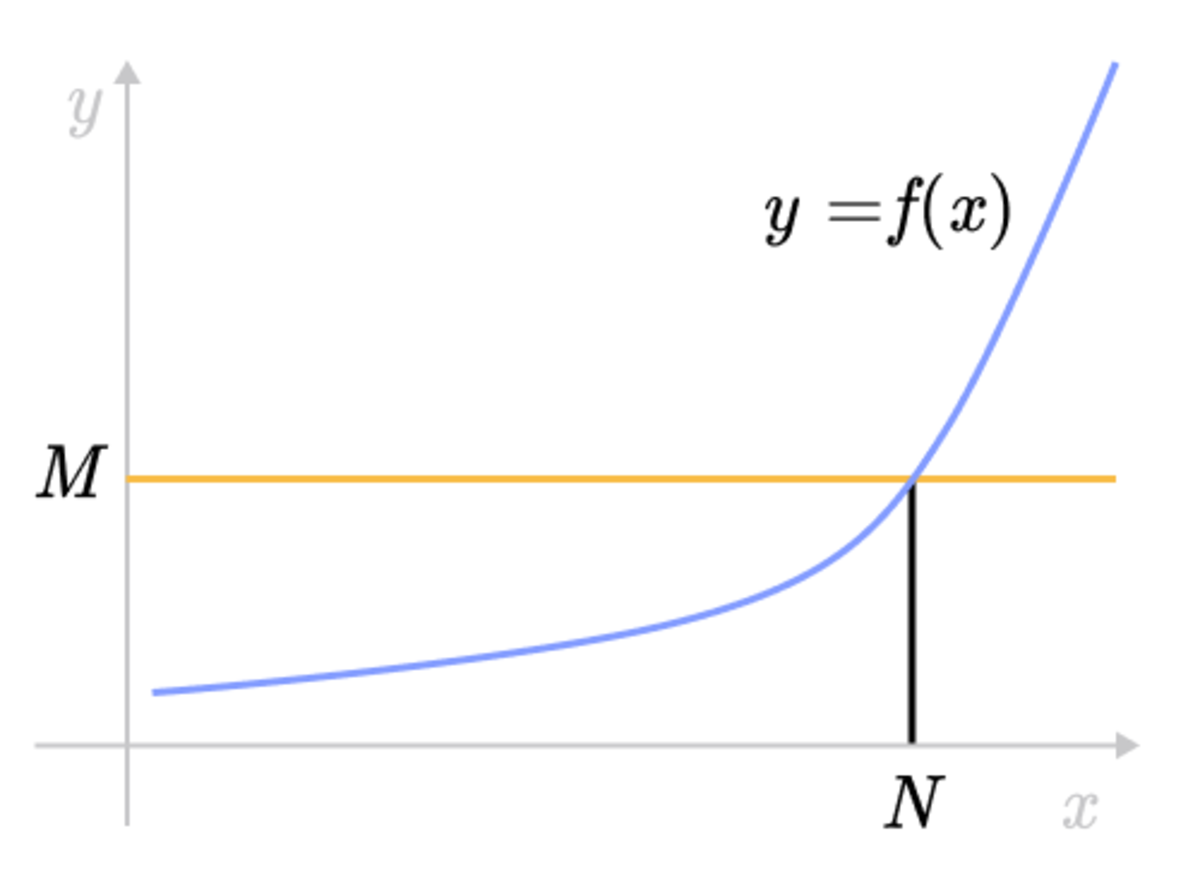



Epsilon Delta Definition Of A Limit Brilliant Math Science Wiki
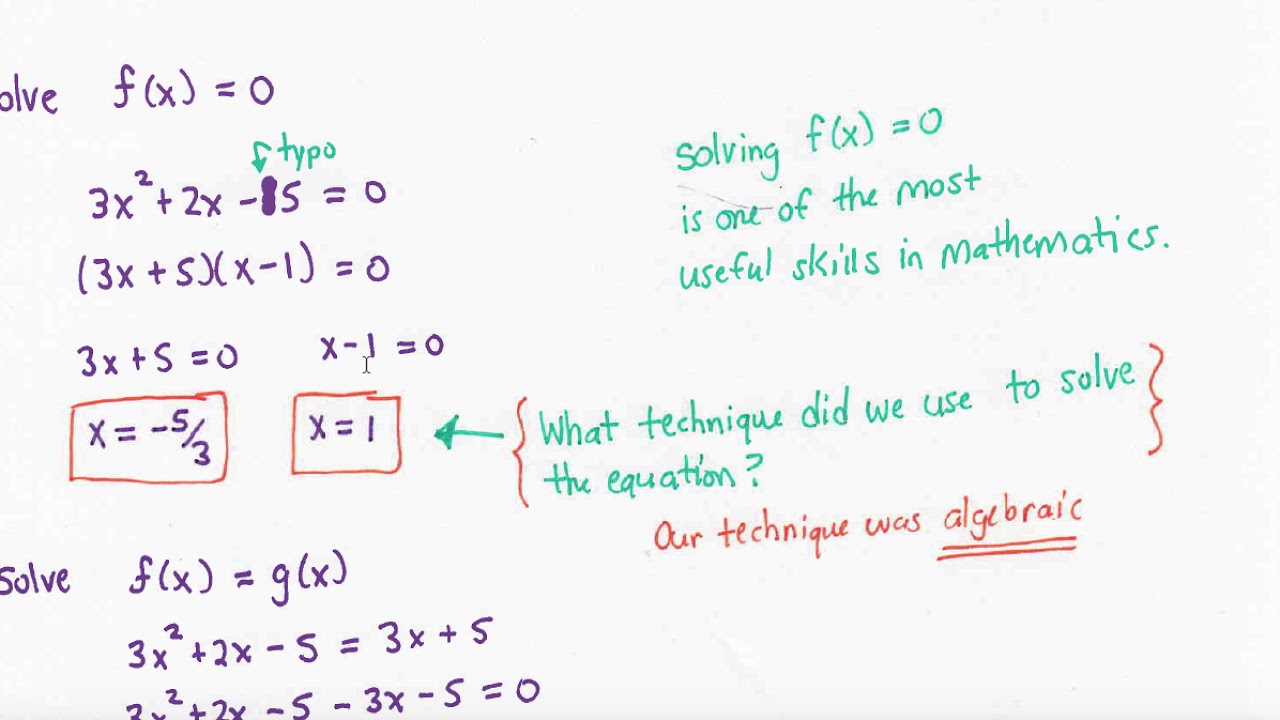



Solving Fx 0 And Fx Gx Youtube
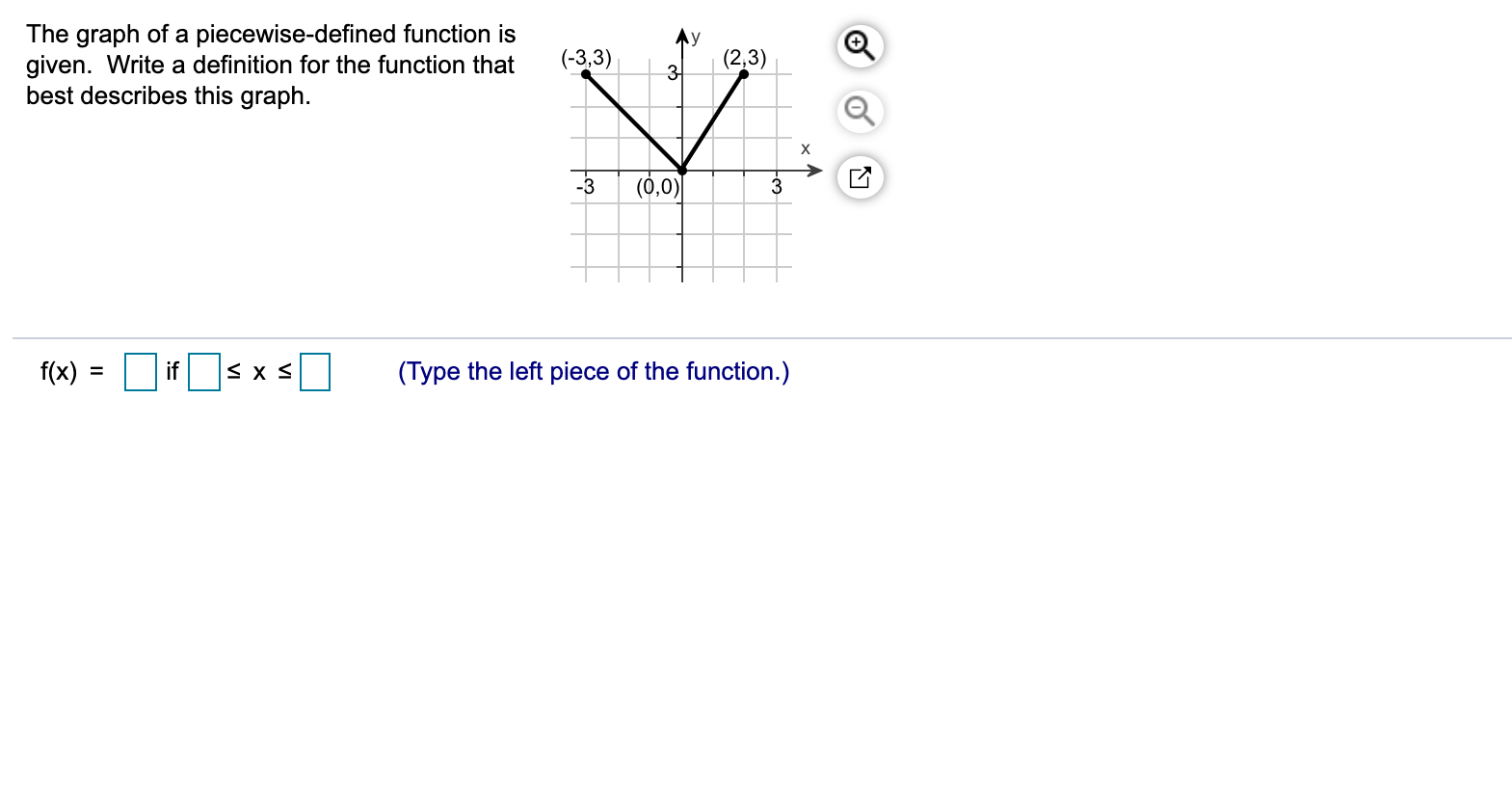



Answered The Graph Of A Piecewise Defined Bartleby



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿